您现在的位置是: 首页 > 教育资讯 教育资讯
高考非谓语动词趣味ppt课件,高考非谓语动词
tamoadmin 2024-06-21 人已围观
简介1.高考单选题,如何判断非谓语作状语这个考点2.高考怎样看这道题考的是非谓语动词还是动词的时态和语态 急!!!3.非谓语动词作定语的用法4.非谓语是什么?5.高考英语语法主要考哪些6.高考英语语法有哪些7.巧学英语“谓语动词”与“非谓语动词”1、Hearing?the?dog?barking?fiercely,away___? 选择:B.?fled?the?thief解析: away?fled?
1.高考单选题,如何判断非谓语作状语这个考点
2.高考怎样看这道题考的是非谓语动词还是动词的时态和语态 急!!!
3.非谓语动词作定语的用法
4.非谓语是什么?
5.高考英语语法主要考哪些
6.高考英语语法有哪些
7.巧学英语“谓语动词”与“非谓语动词”
1、Hearing?the?dog?barking?fiercely,away___?
选择:B.?fled?the?thief
解析:
away?fled?the?thief是倒装句,意思等于the?thieffledaway(小偷迅速逃跑了)
如果把与介词同形的小品副词提前,句子要求倒装,像away这类的副词要加重语气读出来,把原来平铺直叙变成了一种动态效果,意思成了“一下子就如何了”。比如本句,等于汉语的“一溜烟地逃跑了”。另如:
Over?flew?a?bird.?一只鸟嗖的一声飞了过去。
In?ran?a?boy.?一个男孩子飞身跑了进来。
2. A?few?days?after?the?interview,?I?received?a?letter___?me?admission?to?the?university.
解析:
后面的现在分词短语offeringme?admission?to?the?university是a?letter的后置定语。相当于定语从句的功能,因此也可以改写为?which?offered?me?admission?to?the?university(关系代词which?指代?letter,=?the?letter?offered?me?admission?to?the?university[这封信表示愿意接受我进入这所大学])。
如果用?offered,就变成了?the?letter?was?offered,后面也得相应改为?to?me?and?informed?me?that?I?was?admitted?to?the?university,意思是“有人把这封信提供给了我,这封信通知允许我进入这所大学”
高考单选题,如何判断非谓语作状语这个考点
高考英语语法专题讲解-主谓一致
★着重讲解混搭情况,均遵守以下原则:
1. 意义一致原则
主语后跟有以下引起的短语:谓语动词仍与短语前的主语的形式保持一致。
1.1 (together) with: Alice (together) with her parents often goes to the park on Sundays.
1.2 except/but: Every picture except/ but these two has been sold.
Nobody but Mary and I was in the classroom at that time.
1.3 no less than: His sister, no less than you, is wrong.
1.4 rather than: The father, rather than the brothers, is responsible for the accident.
1.5 perhaps : Peter, perhaps John, is playing with the little dog.
1.6 like: He, like you and Xiao Liu is very diligent.
1.7 including/ besides/ as well as
2. 就近原则
2.1 主语由以下连词连接:谓语动词与后一个主语一致:
2.2.1(Either)…or…: Either you or I am going to the movies.
2.2.2 Neither…nor…
2.2.3 Whether…or…
2.2.4 Not only…but (also)
2.2.5 Not…but…
2.2 there be 句型: be 动词与后面第一个名词一致
E.g. There is an apple, two bananas and some oranges on the plates.
2.3副词here, there, now, then, up, down, in, out, away, such连接的全部倒装结构中:谓语动词由动词后面的主语决定
On the wall hang two maps. 墙上挂着两张地图。
On the wall hangs a world of map. 墙上挂着一张世界地图。
Such is the result. 结果就是这样。
Such are the results. 这就是结果
3. 整体原则
3.1 并列主语如果指的是同一个人、同一事物或同一概念时,谓语动词用单数,and后面的名词没有冠词:
The writer and worker is coming to our school tomorrow.
(一个人)
The writer and the worker are coming to our school tomorrow.
(两个人)
Bread and butter is their daily food.
3.2表示时间、距离、价格、度量衡等的复数名词或短语作为一个整体看待时,谓语动词常用单数形式:
E.g. Three years is not a long time.
Ten dollars is what he needs.
Five hundred miles is a long distance.
3.3复数形式的专有名词作为整体看待(人名、地点、国家、组织、书籍、报刊等),动词用单数形式:
E.g. The United Nations has passed a resolution(决议)。
“The Arabian Nights”(《天方夜谭》)is an interesting book.
3.4集合名词people, police ,cattle作主语,谓语动词用复数形式:
E.g. The police are searching for him.
The cattle are grassing (吃草)。
4. 谓单原则
4.1 and连接的并列单数名词前如有each, every, no修饰时,谓语动词要用单数形式。
E.g. Every boy and girl has been invited to the party.
No teacher and no student is absent today.
Many a student is busy with their lessons.
4.2 用many a, more than one 修饰名词时,谓语动词要用单数形式。
E.g. More than one person has made the suggestion.
Many a rough man has been civilized by his wife.
4.3 Each, Either, One, Another, The other, Neither作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式:
E.g. Each takes a cup of tea.
Either is correct.
4.4 由every, some, any, no构成的合成代词作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式:
E.g. Nothing is to be done.
4.5 means, politics, physics, plastics作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式.
5. 具体情况原则
5.1 all, few, more, most, some, any, none, half, the rest等作主语时,既可表示复数意义,也可表示单数意义,谓语动词要根据实际情况而定:
All of the apple is rotten. 整个苹果都烂了。
不可数-> 谓单
All of the apples are rotten. 所有的苹果都烂了。
可数-> 谓复
Most of the wood was used to make furniture.
不可数-> 谓单
Most of the people are from England.
可数-> 谓复
5.2 the + 形容词(或分词)作主语时,常指一类人,谓语动词用复数形式。如指的是抽象概念,谓语动词则用单数形式:
5.3 population当人口讲时,谓语动词用单数形式;当人们讲时,谓语动词用复数:
5.4 the number of + 名词复数,是表示“…的数字”,作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式;
a (large / great) number of + 名词复数,表示许多,作主语时;谓语动词用复数形式:
5.5 有些集体名词如family, team, group, class, audience, 等作主语时,如看作是一个整体,谓语动词则用单数形式;如强调各个成员时,谓语动词要用复数形式:
6. 先行词原则
关系代词who, that, which等在定语从句中作主语时,其谓语动词的数应与句中先行词的数一致。
高考怎样看这道题考的是非谓语动词还是动词的时态和语态 急!!!
判断非谓语作状语这个考点方法:
1.非谓语动词就是不能在句子中做谓语。英语的非谓语动词有:动词不定式(to do)、现在分词(doing)、过去分词 (done)、动名词(doing)。
2.句子的成分一般由主语、谓语、表语、宾语、定语,状语等构成。谓语一般要有动词担任,非谓语动词是不能独立担任谓语的。 但可以担任句子的其他成分,在这里老师给你简要叙述如下:
(1).动词不定式可担任主语,宾语,表语,宾补,定语,状语等。
(2.)动名词可担任主语,表语,宾语,定语等。
(3).现在分词和过去分词可担任定语,表语,宾补,状语等。
例如: He came here to ask for his bike.他来这里要他的自行车。
分析句子成分: he(代词)做 主语, came(动词)做 谓语, here(副词)做状语,to ask for hisbike(动词不等式短语)做目的状语。
非谓语动词作定语的用法
考察非谓语动词的话,若是非谓语作状语,则一般空是在一个完整的句子外;非谓语作定语相对较简单就不用说了。
考查动词的时态和语态,空通常是在句中。
另外你没说是选择题还是完型,或是阅读。
非谓语是什么?
非谓语动词主要包括不定式、动名词和现在分词。
不定式做后置定语,表示将要做(还没有做)。现在分词做定语时,位置不定,如果是一个现在分词,前置,如果是短语后置,表主动。过去分词作定语和现在分词相同,如果是一个过去分词,前哗伐糕和蕹古革汰宫咯置,如果是短语后置,表被动。
式与其所修饰的名词可能是主谓关系。例句:
He was the last one to leave school yesterday.昨天他是最后一个离开教室的。
不定式与其所修饰的名词可能是动宾关系 例句:
Get him something to eat.给他拿点儿东西吃。
She has a lot of work to do in the morning.早上他有很多工作要做。
不及物动词构成的不定式做定语,要加上适当的介词和被修饰的名词形成逻辑上的动宾关系,这里的介词不能省去。
例句:
I need a pen to write with.我需要一支笔写字。
There is nothing to worry about.没有什么值得发愁的。
2.分词作定语时有下面几个特点:
(1)现在分词表示主动意义,过去分词一般表示被动含意。
(2)现在分词表示正在进行,过去分词表示状态或做完(完成)的事。
例句:
He rushed into the burning house.他冲进了正在燃烧着的房子。
The child standing over there is my brother.站在那儿的男孩子是我弟弟。
3.不定式和分词作定语时的时间关系
一般来说,不定式所表示的动作发生在谓语动词所表示的动作之后;现在分词所表示的动作与谓语动词所表示的动作同时发生;过去分词表示的动作发生在谓语动词所表示的动作之前。
例句:
Do you want to see the doctor to be sent for from Beijing?
你要见那位将从北京请来的医生吗?
Do you want to see the doctor working on the case report in the office?
你要见那位正在办公室里写病历的医生吗?
高考英语语法主要考哪些
本文将告诉大家非谓语动词常见的”三态“起源——动词不定态(to+V)、动词进行态(V+ing)、动词完成态(V+ed形式)是怎么来的。
我们知道世界上一切事物都是有生有灭,从酝酿出生、到出生存续、到死亡消逝,一切事物都遵守着这样的自然法则,甚至连语言中的”动词“也不能例外。动词是动作的代称,无论这个动作是可以真实感知的肢体动作,还是不可感知的思维动作,也无论这个动作存续多么短暂或者持续多么长久,其都遵循着出生、存续、死亡这样的过程。如下图所示:
上图从左到右依次为:
1.不定态(todo)表达了动作即将发生的状态;
2.进行态(doing)表达了动作的发生且可感知的延续;
3.完成态(done)表达了动作的结束。
从这里可以看出三大非谓语动词其实就是动作的三个阶段——出生、存续、结束,这就是非谓语动词的起源。
上图自上而下依次为:
1.瞬态隶属于一般态,表达动作的存续转瞬即逝,感觉不到动作的延续;
2.进行态相对于常态又称为非常态,表达动作存续介于瞬态和常态之间,可以感觉到动作的延续;
3.常态相对于进行态/非常态而言,动作呈现了一种常态特性,即长期不变的动作状态或者事实。
这里我们也可以看出动词和时间的关系,上图完整地给出了英语动词的长度体系——从无穷小过度到无穷大,时间的长短决定了动词的状态,也就决定了动词的时态。
上图中的梯形所提到的“不定态、进行态、完成态、一般态”是不含时间内涵的,把这4态分别结合4时、过去时间、现在时间、将来时间、过去将来时间,就得到了英语的16个基本时态,如下图所示:
转换为时态表格如下:
在上图的基础上把“进行态”和“完成态叠加”,又增加了另外的4个完成进行时态,如下图下表所示:
上表转换为下表:
这就是英语非谓语动词到英语谓语动词的进化过程。
有些同学可能会奇怪,“怎么会有不定时态?”
传统的语法是把“不定时态”归属于了“一般时态”,但是本质上这是完全不同的两个时态。
下面用几个公式来表达非谓语动词和谓语动词的关系:
1. 动词原形 + 状态 =非谓语动词
2. 非谓语动词 + 时间 =谓语动词
3. 谓语动词 = 时间助动词 + 状态主动词
4. 状态主动词 = 非谓语动词
以上讲解了非谓语动词的起源,以及非谓语动词到谓语动词的进化过程。
但是非谓语动除了可以做谓语动词的主动词外,非谓语动词还可以做除了谓语动词之外的其它成分,如“主语、宾语、定语、表语、补语、状语”等,在此不在详述。
以上图文表格整理自《英语思维:解密英语语法的原理》图书及视频。
高考英语语法有哪些
一、非谓语动词
“非谓语动词”可分为动词不定式、动名词和分词。它在句子中的作用很多:除了不作谓语外,它可以充当主语、宾语、表语、定语、状语与复合宾语(主语补语或宾语补语)。有些及物动词后面接不带to的不定式作复合宾语。这些动词归纳如下:一感(feel).二听(hear,listen to),三让(have,1et, make),四看(see,watCh,notice,observe)。再加上help somebody(to)do something和美国英语look at somebody do somthing。还有“二让”属特殊:get somebody to do something 与keep somebody doing。而有些及物动词后面接动名词(the -ing form)作宾语。这些动词归纳为一句话:Papa C makes friends。这是由如下动词的开头字母组成:permit,advise, practise,avoid,consider,mind, allow,keep,enjoy,suggest, finish,risk,imagine,escape,need,delay,stand(忍受)。 为了容易记住,也可以编成顺口溜:“允许完成练习,建议避免冒险,考虑延期逃跑,喜欢保持想象,需要反对忍受”。其相对应的动词依次是:permit/allow,finish,practise;
advise/suggest, avoid,risk: consider, delay, escape/miss; enjoy/appreciate, keep, imagine; need/want/require,mind. can't help/can’t stand。
二、复合句
1、学生最容易混淆的是定语从句与同位语从句的区别。
例如:A、The news that our team has won the match is true. (同位语从句)
B、The news that he told us surprised everybody here. (定语从句)
关键的区别在于连接或关系代词that:有意义的是定语, 无意义的是同位。因为引导定语从句的that在从句中作主语或 宾语,而引导同位语从句的that只起到连接词的作用。
2、接着容易混淆的是引导定语从句的关系代词that与 which:that之前是不定(代词)、序数(词)、(形容词)最高级:which之前是介词短语与逗号(非限制性)。
例如:A、All that we have to do is to practise every day.
B、The first lesson that I learned will never be forgotten.
C、I have lost my pen,which I like very much.
D、The house in front of which there is a garden is my home.
三、It的用法
1、It除了代替人和物以外,还可以作形式主语。而真正的主语(不定式、动名词或从句)则放于谓语或表语之后。
例如:It is nor easy to finish the work in two days.
然而有少数表语之后接动名词作真正的主语。这些表语是:无助(no help)、无用(no use)、没好处(no good);工作(hard work)、费时(a waste of time)、又危险(a danger)。
例如:A、It is no use crying over spilt milk.
B、It is a waste of time waiting for him.
2、It还可以作形式宾语。通常下列动词后面可接it作形式宾语:2f2tcjm(find,feel,think,take,consider,judge, make)。
例如:A、He made it clear that he was not interested in this subject.
B、I think it no use arguing with him.
3、It用于强调句式。要强调句子的某一部分(主语、宾语、 状语),可以把it当作先行词。这种句子的结构是:It is(was)+ 被强调部分+that(who)+句子的其余部分。
例如:A、It iS Professor Lin who teaches us English—(强调主语)
B、It was in Shanghai that l saw the film.—(强调状语)
C、It was in 1990 that I worked in the factory.(同上)
但要注意与定语从句的区别。
例如:D、It was 1990 when I worked in the factory.(定语从句)
在强调句式里,我们把强调结构It is(was)…that除去,句子还很完整。如例句C。而例句D就不能。
四、倒装结构
学生容易混淆的是全部倒装与部分倒装。如何区分之,编个顺口溜:副(adv.)介(prep.)提前全倒装,其它句式部分倒;否定提前倒助动,让步状语倒表语;复合句式倒主句,不
倒装的属特殊。下面举例说明:
A、Here comes the bus.(副词提前,全倒装)
B、Here he comes.(代词作主语,不倒装)
C、In front of the house lies a garden.(介词短语提前,全倒装)
D、Never shall I do this again.(否定词提前,部分倒装)
E、Young as he is ,he knows a lot.(让步状语从句,表语倒装)
F、Only when he told me did I realize what trouble he was in.(only 修饰状语,主句倒装)
G、Only he can save the patient.(only修饰主语.不倒装)
H、Not only will help be given to people,but also medical treatment will be provided.(否定词提前,部分倒装)
I、Not only he but also we like sports.(连接两个主语,不倒装)
五、虚拟语气
虚拟语气也是一个难点。所谓虚拟语气是表示说话人的愿望、假设、猜测或建议,而不表示客观存在的事实。它通过句子的谓语动词的特殊形式来表示。现归纳如下:纯假设,用虚拟,动词时态退一级:条件句,分主从,主句谓语前加would (should,could,might);表愿望,用虚拟,wish后面接宾语(从句):现在过去与将来,动词时态退一级:提建议,用虚拟,宾语(从句)动词用(should)do:俩建议,三要求,再加坚持与命令(suggest,advise,demand,require,request,insist,order):It is time和eoukd rather,后接丛句用虚拟:部分主语从句中, 谓语用虚拟结构 (It is necessry /important/natural/natural/strange/strange that……should do)。 下面举例说明:
A、If you came tomorrow,we would have the metting. (条件句虚拟)
B、Without air,there would be no living things.(同上)
C、We wish we had arrived there two hours earlier.(表示愿望虚拟)
D、He demanded that we (should)start right away.(表示建议虚拟)
E、It is(high)time that we left (should leave)now.(特殊从句虚拟)
F、I would rather you gave me the book.(同上)
G、It is necessary that we should clean the room everyday,(主语从句虚拟)
H、He speaks English so fluently as if he were English. (特殊从句虚拟)
总之,语法是从语言实践中总结出来的规则,要边学边寻找规律,以提高学习效率。在学习中不能只记一些语法规则,要进行实践练习。通过练习,可以发现和纠正错误,而且有利于况固所学知识。
巧学英语“谓语动词”与“非谓语动词”
一.非谓语动词
一.不定式:
一)不定式的常考形式:
1) 一般形式:He decided to work harder in order to catch up with the others.
被动形式: He preferred to be assigned some heavier work to do.
语法功能: 表示与谓语动词同步发生
2) 完成形式:He pretended not to have seen me.
被动形式:The book is said to have been translated into many languages.
语法功能:表示发生在谓语动词之前
二)不定式常考的考点:
1)不定式做定语----将要发生
2)不定式做状语----目的
3)不定式充当名词功能---To see is to believe.
三)不定式的省略
1)感官动词 see, watch, observe, notice, look at, hear, listen to, smell, taste, feel
+ do 表示动作的完整性,真实性;
+ doing 表示动作的连续性,进行性
I saw him work in the garden yesterday.
昨天我看见他在花园里干活了。(强调"我看见了"这个事实)
I saw him working in the garden yesterday.
昨天我见他正在花园里干活。(强调"我见他正干活"这个动作)
" 感官动词后面接形容词而不是副词:The cake tastes good; It feels comfortable.
2) 使役动词 have bid make let 等词后不定式要省略但同1)一样被动以后要还原to
I 'd like to have John do it.
I have my package weighed.
Paul doesn't have to be made to learn.
3) help help sb do help sb to do help do help to do
四)有些动词后只跟不定式如:
want,wish,hope,manage,promise,refuse,pretend,plan, offer,decide,agree,expect allow sb to do, cause sb to do , permit sb to do, enable sb to do
force sb to do. be more likely to do love to do warn sb to do be able to do
be ambitious to do. begin to do . start to do
We agreed _______ here,but so far she hasn't turned up yet.(NMET
1995)
A.having met B.meeting C.to meet D.to have met (Key:C)
五) 有的时候to后面要接-ing形式
accustom (oneself) to; be accustomed to; face up to; in addition to; look forward to; object to; be reduced to; resign oneself to; be resigned to; resort to; sink to; be used to; be alternative to; be close/closeness to; be dedication/dedicated to; be opposition/opposed to; be similarity/similar to.
三、need/want 后的-ing形式具有被动的意思。其中,want不太常用。
He needs (a lot of) encouraging.
二. 动名词: 具有动作性特征的名词
1)是名词 seeing is believing
2)具有动词性特征可以带宾语 starving troops is necessary.
一)动名词的形式:
一般形式:I don't like you smoking.
完成形式:I regret not having taken your advice.
被动形式:This question is far from being settled.
二) 动名词常考的点
1)动名词做主语谓语动词为单数
2)在动名词和不定式中,做为介词的宾语是动名词
3)动名词的否定直接在其前加否定词,通过代词的宾格或所有格形式给出逻辑主语.
I would appreciate_______ back this afternoon.(MET 1992)
A.you to call B.you call C.you calling D.you're calling(Key:C your calling 也对)
I regret not having taken your advice.
4)有些词后只能接动名词
admit; appreciate; avoid; celebrate; consider; contemplate; defer; delay; deny; detest; discontinue; dislike; dispute; enjoy; it entails; escape; excuse; explain; fancy; feel like; finish; forgive; can't help; hinder; imagine; it involves; keep; it means; mention; mind; miss; it necessitates; pardon; postpone; practice; prevent; recall; report; resent; resist; risk; suggest; understand...
另外还有一些接-ing形式的常用说法:
it's no good; it's no/little/hardly any/ use; it's not/hardly/scarcely use; it's worthwhile; spend money/time; there's no; there's no point in; there's nothing worse than; what's the use/point...
5有些词后加不定式和动名词均可
remember, forget, try, stop, go on, cease, mean后面用不定式和-ing形式,意义截然不容。
I remembered to post the letters. (指未来/过去未来的动作)
I remembered posting/having posting the letters (我记得这个动作)
forgot remember的用法类似。
I regret to inform you that… 我很遗憾地通知你…
I regretted having left the firm after twenty years. 为了"二十年前的离开"而遗憾。
try to 努力 You really must try to overcome your shyness.
try -ing 试验 Try practicing five hours a day.
I mean to go, but my father would not allow me to. [打算、想]我想去,但我父亲不让我去。
To raise wage means increasing purchasing power. [意味着]赠加工资意味着增加购买力。
prefer的用法:
我宁愿在这里等。
3 分词:
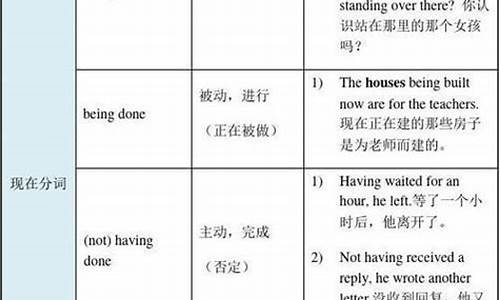
现在分词主动进行,过去分词被动状态
现在分词的形式:
1)一般式: Do you see the man talking to the dean(主任)? (与谓语动词同步发生)
2)完成形式:Not having made adequate preparations, they failed. (发生谓语动词之前)
3)完成被动形式:Having been adapted, the script seems perfect.( 发生谓语动词之前且表示被动)
过去分词
1) 过去分词表示被动:Fight no battle unprepared.
2)过去分词的进行形式:You'll find the topic being discussed everywhere. (强调正在被做)
这三种非谓语动词,都可以构成复合结构,非谓语动词所修饰的成分是这些非谓语动词的逻辑主语。他们之间的一致关系--主动还是被动,往往就是考点。独立主格结构中,要注意的是分词与他前面的逻辑主语之间的主动被动的关系。
二:虚拟语气和情态动词
情态动词的基本用法及其区别
最近几年高考试题中常常借助语境来考查情态动词的基本用法及其区别,因此在平时学习时准确理解和掌握情态动词的基本用法十分重要。情态动词的用法复杂多变,在高考试题中,命题者常常利用语境和句子之间意义上的细微差别来考查学生对情态动词的理解和掌握。对于情态动词,除了要求考生能够准确掌握它们的基本用法外,还要充分利用高考试题所设置的语境来分析句子之间所体现的特殊关系。下面就近几年来高考试题中出现的情态动词的考点进行归纳分析,以便同学们复习掌握。
一、用"情态动词+have +done"结构表示对过去动作的推测,高考试题中常用过去时态或过去的时间状语给以暗示。情态动词的这一用法可以用 "对立统一"来概括。
1.当试题的前句和后句在动作和意义上相互补充说明,且整个句意在动作和时间上是一个整体时,我们可用"统一"关系来解决这样的试题。常见的结构有:
must have done:
表示对过去动作的肯定推测,常译作"一定做了……",只能用于肯定句中。其否定形式为can't/couldn't have done?
疑问式为Can/Could...have done?。
could /might have done:表示对过去发生的动作的可能性推测,常译作"可能做了……"。如:
1) My sister met him at the Grand Theater yesterday afternoon, so he
_____ your lecture. ?(上海 2000)
A. couldn't have attended
B. needn't have attended
C. mustn't have attended
D. shouldn't have attended
本题选A。
2) Jack ____ yet, otherwise he would have telephoned me. (上海'97
A. mustn't have arrived
B. shouldn't have arrived
C. can't have arrived
D. need not have arrived (C)
2.当试题的前后句在动作和意义上构成转折关系时,常借助"but, however, instead"等词来表示过去的动作与客观事实不符,这时我们就可以用"对立"关系来解决这样的试题。这种结构常见的有:
should have done / ought to have done:表示过去本应该做某事而实际上没有做。
should not have done / ought not to have done:表示过去本不应该做某事但事实上却做了。
由句中的连词but可知前后句之间是对立关系,分析题意可知本题应选C。
二、考查情态动词基本用法之间的比较和辨析。最近几年高考试题中常借助具体的语境来考查考生对那些最常见的情态动词的基本用法的理解和掌握,因此在做这样的试题时应认真分析语境中所含的实际意义,并结合情态动词的基本含义和用法做出正确的选择。
虚拟语气
" 最自然的虚拟状态:由should/would+原型时态(不含时间只含状态)
本质上是过去将来时:即,时间固定在过去将来,状态不同:一般、进行、完成、完成进行。
这时"虚拟语气"的产生往往是因为我们要表达"本来应该……"(而现在却还没有……)
(本来可以……,本来能……)
一些常见的句型中,就会出现这种虚拟语气,而处于从句之中,should 常常被省略掉
o suggest, advise, propose, recommend, plan;
o demand, order, direct, arrange, command, decide;
o require, request;
o think, expect, believe, insist, suspect.
由于他们的含义中包含"建议,假设,应该"这类的含义,所以,由他们引起的从句中,就会包含有should+原型时态构成的虚拟语气。
这些动词(以及他们的名次形式,分词形式)引起的从句还有其他的变形
主语从句,表语从句,同位语从句
It's suggested that…
My suggestion is that…
The only suggestion that...
The only suggestion I can give you now is that…
一些形容词引起的表语从句中,也会有同样的情况
important; necessary; essential
It's natural ; strange; incredible that
a pity; a shame; no wonder
? 由lest, for fear that, in case 引起的从句中多使用should
" 表达与事实相反
1. 与现在相反:使用[过去时]:
I wish I were not here! (一般现在'一般过去)
Suppose we were not here.
He loved me as if I were his own son. (一般现在'一般过去)
Hope I weren't always losing things! (现在进行'过去进行)
If only/If I hadn't been there! (现在完成'过去完成)
What if I hadn't been waiting right here! (现在完成进行'过去完成进行)
常考句型:It's (high) time (that)…; would rather (that)…
这两个从句,只能表达对现在的看法,所以,从句中只有一般过去时。
2. 与过去相反:过去完成时;
3. 与将来相反?将来的事情没有发生,所以只能推测且实现可能很小
I wish he could not smoke any more.
不过,由于可以用be to表示将来;所以,虚拟语气中经常出现were to;也是CET-4的常考语法点。
" 虚拟条件句
o if 部分,做一个与事实相反的假设(所以只有一般过去和过去完成)
o 主句部分,这是表示基于这个假设的推测,一般使用情态动词would,少数情况下使用could/might/should。
o 注意:两个部分之间,是有逻辑关系,而在两部分的谓语动词时态上,没有必然的联系。
" 注意,虚拟条件句中的if可以省略,造成were/had提前,产生倒装。
" 隐含的非真实条件 :由特殊的词给出条件: with, without, in , but for, otherwise, or
How could I be happy without you? In his shoes, I would kill myself.
But for the storm, we would have arrived.
三、一致关系
一)主谓一致
1. 主谓一致(与插入语无关)
1主谓的分隔原则:主谓之间可以用定语从句或者省略的定语从句分隔。
2定语从句中的主谓一致:
3随前一致:
n. + together with n2
as well as
including
along with
with / of
accompanied with / by
4就近原则:n1 or n2 +v(就近原则)
either n1 or n2
5可数n1 and 可数n2+v(pl)
不可数n1 and 不可数n2+v(pl)
例外:war and peace is… war and peace是一个整体
但是如果主语表示的是同一个概念,同一人,同一事的时候,谓语动词用单数,这种结构的特征是and连接的两个词只有一个冠词。
The iron and steel industry is very important to our country.
The head master and mathematical teacher is coming.
The head master and the mathematical teacher are coming.
类似的还有:law and order bread and
butter black and white
To love and to be loved is …
A lawyer and a teacher are…
A lawyer and teacher is …
6随后原则:not A but B / not only A but also B+v.(与B一致)
7百分比结构:most , half , rest , some , majority , one+persent
of+n1+v.(由n1决定
8倒装结构的主谓一致:
a)There be +n 由名词决定动词
b)Among , between等介词位于句首引起倒装结构:
Among / Between …+系动词+n. (由名词决定动词)
9The+adj的主谓一致:
a)当表示"一类人",
b)当表示某一抽象概念时
The good is always attractive.
10 To do/doing/主从+vs
*More than one+n
many a +n.
a day or two
二)、倒装
1 全部倒装
是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用与一般现在时和一般过去时。常见的结构有:Up went the plane = the plane went up.
1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, come, go, lie, run。
2) 表示运动方向的副词(back, down, off, up)或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。
注意:1) 上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能倒装。Here he comes. Away they went. 2) 谓语动词是be的时候,不能倒装。 Here it is. Here you are.
3) 形容词短语/分词短语位于句首,引起倒装
*typical of characteristic of
*coinciding with + n
4) 表示地点范围的介词短语位于句首,谓语动词为系动词,一定引起倒装
In…(表语)+系动词+主,主同。
*在倒装句型答案中不能出现there
*常考介词要倒装:among between in at beneath
常考的系动词:be lie exist remain rest
部分倒装
1. 否定 adv 位于句首,引起倒装:not only, not until, hardly, scarcely,
seldom, rarely, no sooner…than
1) not until + 时间 + 主谓倒装,not until + 句子+主谓倒装
2) only+状语位于句首
only +ad. eg: recently
prep.短短语 eg: in recently years
从句 eg: when clause
only一个词本身不倒装
3) 在比较级结构中,than后面可以倒装,也可以不倒装。
部分倒装是指将谓语的一部分如助动词或情态倒装至主语之前。如果句中的谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则需添加助动词do, does或did,并将其置于主语之前。
? 1) Neither, nor, so 表示前面句子的共同否定或者肯定,产生倒装,一般主动词提前,谓语动词的其他部分就
4) as / though引导的让步从句必须将表语或状语提前 (形容词, 副词, 分词, 实义动词提前)。
as〔让步〕虽然,尽管〔词序倒装。语气比 though 强〕。
Successful as he is, he is not proud. 他虽成功,却不骄傲。
Women as she is, she's every brave.
Try hard as he will, he never seems able to do the work satisfactorily.
注意:A) 句首名词不能带任何冠词。B) 句首是实义动词, 其他助动词放在主语后。如果实义动词有宾语和状语, 随实义动词一起放在主语之前。
5) 其他部分倒装
a) so… that 句型中的so; such… that句型中的such位于句首时,需倒装。
So frightened was he that he did not dare to move an inch.
b) 在某些表示祝愿的句型中:May you all be happy.
c) 在虚拟语气条件句中从句谓语动词有were, had, should等词,可将if 省略,把 were, had, should 移到主语之前,采取部分倒装。Were I you, I would try it again.
四、复合句
从句可分为:
? 名词性从句' 主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句
? 形容词性从句'定语从句
? 副词性从句'状语从句
" 常考的关系代词:that; which; who/whom/whose; where; when; what; as。
" 常见的同位语从句现行词(that之前的抽象名词):fact, idea, news, hope, conclusion, evidence, opinion, problem, thought, understanding…
" 常用的引导词
o 时间状语从句:while; when; before; whenever; as; after; till; until; since; once; ever since; as/so long as; as soon as; no sooner… than; hardly… when; scarcely/barely… when; the moment/minute/instant; on (the point of) doing…
o 地点状语从句:where; wherever
o 原因状语从句:because; since; as; seeing that; considering that; now that; in that; for fear that; lest; owing to the fact that; because of the fact that; due to the fact that…
o 方式状语从句:as; as if; as though; how; save that…
o 比较状语从句:as; than; as… as; not so… as; hardly… than;
o 结果状语从句:so that; so… that; such… that; so as to…
o 条件状语从句:if; unless; in case; so long as; so far as; provided/providing/that; supposing; granted/granting that…; giving that…
o 让步状语从句:though; although; even if; even though; whether; as; however; no matter (what, how, when); for all that; in spite of the fact that; granted that; regardless of the fact that…
o 目的状语从句:that; so that; in order that; lest; for the fear that; in case…
定语从句:
which 引导的定语从句结构
1)which是关系代词,which后面应该加缺主语或者宾语的句子,
在这个句子中,which要作成分,作主语或者宾语
2)in which+完整的句子
which在定语从句中作in的宾语,所以不能作后面句子的主语
3)名词+of which+谓语动词
of which来修饰名词,名词在定语从句中作主语,所以后面直接跟谓语动词
I have five books three of which are borrowed from Mary.
4)介词+ which +to do 其功能相当于定语从句。
The key with which to open the door is lost.
5)定语从句的省略结构:
1. 如果that / which在定从中作 宾语,可以省略.
sub+vt+n+(which / that)+sub+vt
→s+vt+n+s+v
s+vt+n1+n2+vt
*当做题时,若发现两个名词在一起,但是似乎连不上,则一定省略that /
which,则动词为vt,做谓语。
6)定从的特殊省略
the way (in which) + 句子
the reason (why that)+句子 均为完整句
the time (that / when)+句子
I do remember the first time (that省) I ever heard the sweetest voice in the world.
By the time省that+句子,句子。
7)定从的主系省略(主+系可同时省)
即:which be , who be , that be可同时省
状语从句省略结构
这种省略从句主语的方式理论上需要满足以下两个条件:
第一、特定的状语从句引导词:although though even though when while if as
第二、从句主语和主句主语必须保持一致;
第三、从句的谓语必须是be动词,主语和be动词同进同出,比如上面的they和are要么同时省略,要么同时保留。
高考英语插入语及插入句的用法
在NMET中,插入语屡见不鲜,由于插入语通常与句中其它成分没有语法上的关系,因此给考生的理解带来一定困难。插入语多半用逗号与句子隔开,用来表示说话者对句子所表达的意思的态度。插入语可能是一个词、一个短语或一个句子。
一、常用做插入语的副词
indeed的确, surely无疑, however然而, obviously显然, frankly坦率地说, naturally自然, luckily (或happily) for sb.算某人幸运, fortunately幸好, strangely奇怪, hone stly真的, briefly简单地说等。
1. Surely, she won?t go to China Telecom with you.
当然她不会和你一起去中国电信。
2. Strangely, he has not been to China Unicom. Still more strangely, he has not called me.
奇怪,他未来过中国联通。更奇怪,他没给我打电话。
3. Fortunately, I found the book that I?d lost.
幸亏我找到了已丢失的那本书。
二、常见的作插入语的形容词或其短语
true真的, funny真可笑, strange to say说也奇怪, needless to say不用说, most impor tant of all最为重要, worse still更糟糕的等。
1. Strange to say (或True), he should have done such a thing.
说也奇怪(或真的),他竟然做出这样的事。
2. Most important of all, you each over?fulfilled your own task.
更为重要的,你们各自超额完成了自己的任务。
三、常用作插入语的介词短语
in a few words(或in sum, in short)简而言之, in other words换句话说, in a sense在某种意义上, in general一般说来, in my view在我看来, in his opinion(judgment)按照他的意见(判断), in conclusion总之, in summary概括地说, in fact事实上, in the first place首先, in addition此外, of course当然, to our knowledge据我们所知, to my joy(delight, satisfaction)使我欣慰(高兴、满意)的, to their surprise(astonis hment, amazement)使他们惊奇的, to her regret (disappointment)使她遗憾(失望)的, for instance(或example)例如, as a matter of fact事实上等。
巧学英语“谓语动词”与“非谓语动词” 摘 要:纵观历年高考,英语动词的考查可谓重中之重。然而,大部分的高中生在英语学习过程中却常常被各种动词的形式而困扰。下面,我就大部分学生最为头疼的动词问题从以下几方面谈谈
关键词:英语 谓语动词 非谓语动词
一、英语动词的分类
众所周知,英语中的动词可以充当主语、谓语、宾语、表语、定语、状语和补足语等很多成分。我们不妨以谓语为标准,主语、宾语、定语、状语和补足语都是谓语以外的成分。为了方便起见,我们把能做谓语的动词称为“谓语动词”,反之,我们把主语、宾语、表语、定语、状语和补足语这些谓语以外的'成分统称为“非谓语动词”。
我们所学过的动词形式有很多,如:动词原形、第三人称单数、过去式、不定式、过去分词和现在分词等。其中,动词不定式、现在分词和过去分词这三种动词形式不能作谓语,其它动词形式能做谓语。因此,英语动词分为谓语动词和非谓语动词。非谓语动词包括动词不定式、现在分词和过去分词,谓语动词则指动词不定式、现在分词和过去分词以外的动词形式。
二、英语动词考查的重点
根据英语动词的分类可知,英语动词考查的重点之一就是区分所选择的动词是“谓语动词”还是“非谓语动词”。另外,根据动词的含义可知,动词就表示动作,一定存在主动和被动。因此,英语动词考查的重点之二就是考查动词是主动还是被动的形式。
三、巧解英语动词试题
针对英语动词考查的重点之一,在实践中我们可以考虑以下两点:第一、经过分析,所选择的动词如果作谓语就把不作谓语的动词不定式、现在分词和过去分词排除掉;第二、如所选择的动词不作谓语就从动词不定式、现在分词和过去分词中选择。
针对英语动词考查的重点之二,我们要从动词作谓语和不作谓语两方面来考虑。第一、如果所选动词作谓语,就考虑句子的主语与所选动词之间是主动还是被动关系,从而确定句子是主动语态还是被动语态。第二、如果所选动词不作谓语,也要考虑动词所充当的成分。但重点考虑的成分有三个,分别为:定语、状语和宾语补足语。具体说,如果所选动词作定语,就考虑动词所修饰的中心词与所选动词之间是主动还是被动;如果所选动词作状语,就考虑句子的主语与所选动词之间是主动还是被动;如果所选动词作宾语补足语,就考虑宾语与所选动词之间是主动还是被动。 四、英语动词选择的难点
针对英语动词的考查点,发现选择难点如下:
难点一:确定主动语态还是被动语态,重点弄清各种时态的主动及被动语态(见表一)。
难点二:动词不作谓语时,重点弄清哪些动词形式为主动、那些动词形式为被动形式。针对这点,我们要考虑三点:一、动词不作谓语时的动词形式要从动词不定式、现在分词和过去分词中选择;二、要弄清动词不定式、现在分词和过去分词分别有哪些形式(见表二);三、要考虑动作所发生的时间是过去、现在还是将来,相对应的涉及到的动作就分别为做过、在做还是要做,这要把动词不定式、现在分词和过去分词综合到一起考虑。(见表三)。
五、真题演练
1.To his great joy,the day he had been looking forward to at last .
A.came B.coming C.has come D.had come
2.When the two books,I won’t pay more attention to the prices..
A. c omp a r i n g B. t o c omp a r e C.compared D.having compared
3.We should learn more from the people as national heroes.
A.knowing B.having been known C.known D.to be known
4.To be well prepared for the meeting next week,the manager is busy collecting necessary information.
A.held B.to be held C.being held D.having held
5.With the guide us ,we had little difficulty finding the destination.
A.to help B.having helped C. helping D.helped
Keys:A A C B C ;









