您现在的位置是: 首页 > 教育新闻 教育新闻
高考英语必备动词_高考常考英语动词短语
tamoadmin 2024-07-19 人已围观
简介1.英语高考必须掌握的所有系动词,谢谢,是所有的2.高考英语语法的考点都有哪些3.高考英语语法有哪些4.高考需要掌握的不及物动词有哪些(英语)5.跪求高考英语考到的几大重要动词时态高考英语写作常用动词及经典句型1.不及物动词 go come work 2.及物动词 he do make expect(want) tell teach show see hear find watch think
1.英语高考必须掌握的所有系动词,谢谢,是所有的
2.高考英语语法的考点都有哪些
3.高考英语语法有哪些
4.高考需要掌握的不及物动词有哪些(英语)
5.跪求高考英语考到的几大重要动词时态
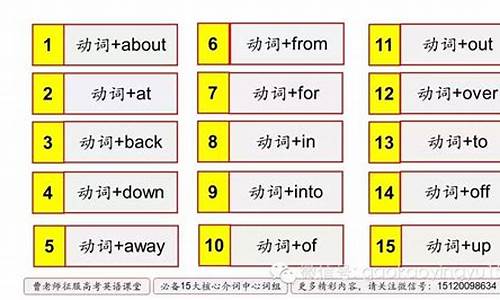
高考英语写作常用动词及经典句型
1.不及物动词 go come work
2.及物动词 he do make expect(want) tell teach show see hear find watch think get …
She showed him how to grasp the main idea of articles.
I taught myself English when I was at your age.
二.常用句型
1. There be( exist, live, lie , stand…) sb./ sth.
2. sb. he ( has / had ) sth.
3. sb. find / think /feel + it + n./ adj.+ (for sb. ) to do sth.
We think it our duty to work hard.
She finds it necessary to take down notes while listening.
They feel it important to he some working experience.
4. ~ the most +形容词+名词+ (that) +主词+ he ever + seen ( known/heard/had/read… Helen is the most beautiful girl that I he ever seen.
Mr. Chang is the kindest teacher that I he ever had.
5、Nothing is + more +形容词+ than to + V
Nothing is more important than to receive education.没有比接受教育更重要的事。
6、~ cannot emphasize the importance of ~ too much.(再怎么强调...的重要性也不为过
We cannot emphasize the importance of protecting our eyes too much.
7、There is no denying that + S + V ...(不可否认的...)
There is no denying that the qualities of our living he gone from bad to worse.
There is not denying that successful business lies in a healthy body and mind.
8、It is universally acknowledged that +句子~~(全世界都知道...)
It is universally acknowledged that trees are indispensable to us.
9、There is no dou that +句子~~(毫无疑问的...)
There is no dou that our educational system lees something to be desired.
毫无疑问的我们的教育制度令人不满意。
10、An advantage of ~is that +句子(...的优点是...)
An advantage of using the solar energy is that it won‘t create (produce) any pollution.
11、The reason why +句子~~~ is that +句子(...的原因是...)
The reason why we he to grow trees is that they can provide us with fresh air.
The reason why we he to grow trees is that they can supply fresh air for us.
12、So +形容词+ be +主词+ that +句子(如此...以致于...)
So precious is time that we can’t afford to waste it.
13、Adj / n.+ as + Subject(主词)+ be, S + V~~~(虽然...)
Rich as our country is, the qualities of our living are by no means satisfactory.
{by no means = in no way = on no account一点也不}
虽然我们的国家富有,我们的生活品质绝对令人不满意。
Child as she is, she pays much attention to her behior.
14、The + ~er + S + V, ~~~ the + ~er + S + V ~~~
The + more + Adj + S + V, ~~~ the + more + Adj + S + V ~~~(愈...愈...)
The harder you work, the more progress you make.
The more books we read, the more learned we become.
15、By +doing sth., sb. can do sth.(借着...,..能够..)
By taking exercise, we can always stay healthy. 借着做运动我们能够始终保持健康。
16、It is said /reported / known / thought/ believed (that)
It is believed (that) reading increases our knowledge and broadens our mind.
17、On no account can we + V ~~~(我们绝对不能...)
On no account can we ignore the value of knowledge. 我们绝对不能忽略知识的价值。
18、It is time + S +过去式(该是...的时候了)
It is time the authorities concerned took proper steps to solve the traffic problems.
19、根据我个人经验?…
According to my personal experience, …= Based on my personal experience, …
According to my personal experience, smile has done me a lot of good.
20、There is no one but ~~~(没有人不...)
There is no one but longs to go to college.没有人不渴望上大学。
21、It is + n / adj + that / to do…
It is a must that everybody should know how to use computers.
It is convenient for us to be able to use computers
22、That is the reason why ~~~(那就是...的原因)
Summer is sultry. That is the reason why I don‘t like it.
23. For the past +时间,S +现在完成式...(过去...年来,...一直...)
For the past two years, I he been busy preparing for the examination.
24、Since + S +过去式,S +现在完成式。
Since he went to senior high school, he has worked very hard.
25、It pays to + V ~~~(...是值得的。)
It pays to help others. 帮助别人是值得的。
26、It is no use (good) doing…
It’s no good talking without thinking carefully.
27. It is necessary/ important/essential that + sb. (should) + do sth.
It is important that we (should) keep the public places clean.
28、What a + Adj + N + S + V!= How + Adj + a + N + V!(多么...!)
What an important thing it is to keep our promise!
How important a thing it is to keep our promise!遵守诺言是多么重要的事!
29、not only…but also
In just three years, she had not only finished all the lessons, but also received her
Doctor’s degree.
Forests can not only fresh the air but also reduce noise.
30、Due to/Owing to/Thanks to + N/Ving, ~~~(因为...)
Thanks to his encouragement, I finally realized my dream.
31、I am greatly convinced (that) = I am greatly assured (that) 我深信…
I am greatly convinced that prevention is better than cure. 我深信预防是于治疗
32、not…until
I didn’t know the truth until she told me what hened.
Yesterday I didn’t go to sleep until midnight.
三.常用短语
1. do good to(对...有益),do harm to(对...有害)
Reading does good to our mind.读书对心灵有益。
Overwork does harm to health.工作过度对健康有害。
2. would (not) like to do sth.
(don’t ) feel like doing sth.
had better ( not ) do sth.
would rather ( not ) do sth.
prefer to do…rather than do
Compared with women, men always prefer to sleep at home rather than spend so much time shopping.
Tom prefers to stay up late to finish the work rather than lee it done the next day.
3. ~ enable + Object(受词)+ to + V(..使..能够..)
Listening to music enable us to feel relaxed. 听音乐使我们能够感觉轻松。
4. be + forced/obliged + to + V(不得不...)
Since the examination is around the corner, I am obliged to give up doing sports.
5. spare no effort to do sth.
= do one’s utmost to + V = do one’s best(不遗余力的,尽全力去...)
We should do our utmost to achieve our goal in life.
We should spare no effort to beautify our environment.
6. be closely related to ~~(与...息息相关)
Taking exercise is closely related to health.做运动与健康息息相关。
7. He a great influence on ~~~(对...有很大的影响)
Smoking has a great influence on our health.
8. Get into the habit of + Ving= make it a rule to + V(养成...的习惯)
We should get into the habit of keeping good hours.
9.as if
He talks a lot as if he knew everything. It seems as if I am the first one arriving at school.
10.Lee much to be desired(令人不满意)
The condition of our traffic lees much to be desired.我们的交通状况令人不满意。
11.be based on(以...为基础)
The progress of society is based on harmony. 社会的进步是以和谐为基础的
英语高考必须掌握的所有系动词,谢谢,是所有的
动词类:
1. “看” :look; see; watch; observe; notice; catch sight of; stare; glare; glance; glimpse; see a film; watch TV;
2. “说” :telll sth to sb.=tell sb sth; talk with sb about sth; say
sth; speak in English; whisper sth to sb; inform sb of sth; reason
/talk/persuade sb into doing sth; bargain; cha; repea; explain; warn;
remind; discuss; debate; figure; declare; claim; mention; admit; deny;
describe; announce; introduce; complain
3. “叫” :cry; call; shout; scream; moan; sigh; quarrel
4. “问” :ask; interview; express; question
5. “答”:answer; respond; reply
6. “听”:listen to; hear; pick up; overhear
7. “笑”:smile; laugh; burst into laughter; burst out laughing
8. “哭”:cry; shed tears; weep; sob; burst into tears /burst out crying
9. “吃/喝” :eat/drink; sip; he a meal; he supper; toast; taste; treat sb to; help oneself to
10. “穿” :put on; wear; he on; be dressed in; make-up; get changed; be in red; take off ; remove
11. “行” :walk ; run ; climb; jump; skip; slip; come/go; enter; move; drive; ride; fly; crawl
12. “坐” :sit down; be seated; seat oneself; take a seat/ stand; lean
13. “睡/休息” :lie /on one’s back/on one side/ on one’s stomach; stay
in bed; he a rest; take a nap; be asleep; bend; turn over; rest
14. “写” :dictate; write sth; describe; drop a line; draw; take down/write down
15. “拿/放”: take; bring; hold; carry; fetch; lif; put; lay; pull; push
16. “抓” :take hold of; seize; grasp; scratch
17. “打” :hit; beat; strike; blow; attack
18. “扔” :throw; drop; fall; we; shake
19. “送” :send; deliver; give; offer; see off
20. “摸/抱” :ouch; fold; embrace; hug; hold; in one’s arms
21. “踢/碰” :kick; knock; tip
22. “找/查” :find; look for; find out; discover/explore; hunt for;
search for seek / seek for in search of; search sb; search sp. for sth;
check; examine; test; inspect
23. “得” :get; oain; acquire; gain; possess
24. “失” :lose; be lost /be missing; gone; great loss
25. “有” :he; own; conquer; occupy =possess
26. “无” :nothing left; the remaining thing; disear; be missing /gone
27. “增/减” :rise / go up /drop; raise; bring down /reduce; increase/decrease
28. “买/卖” :buy; purchase; afford; pay; pay off ; pay for; sell; on
sale; bargain; bill / cheque / cash/credit card/notes/coins; discounts
29. “存在/消失” :come into being; exist; ear; survive ; live; show;
turn up; disear; die; die out; pass away; be out of sight
30. “变化” :develop; improve ; become; grow; go+ bad /wrong/ sour
/without( negative adj.) turn + colour; change /change into; reform
31. “成功/失败” :make it; succeed; make progress; come true; realize
one’s dream; win; lose; fail to do; defeat; suffer loss; beat; turn sth.
into reality
32. “努力” :try /manage; make efforts; attempt ; do ones best; do as much as one can to do
33. 祝贺:congratulate sb. on sth.; celebrate; observe; get together
34. 敬佩:admire; respect; show respect for/to; adore; envy /be jealousy
35. 赞美/批评:praise; think highly of; blame sb for sth; sb is to
blame; criticize /scold sb. for sth.; he a low opinion of sb; speak
ill of
36. 喜/恶:like; love; be fond of ; be keen on; be crazy about; adore; be into; prefer; enjoy; dislike hate; ignore
37. 到达:arrive at; reach; return to; get to; stay in sp.; visit; lee; lee for
38. 受伤:hurt ; injure; wound; cut; kill; drown; bleed; get burnt; suffer from; suffer a loss
39. 损坏:damage; destroy; ruin; break down; crash; be broken
40. 修复: repair; rebuild; restore; fix; recover oneself
41. “认识的过程” :feel; sense; guess; suppose; wonder; dou; know
/learn realize understand remember; be familiar with; recall; recite;
ly to
42. 认为;判断:think; believe; consider; find; feel; conclude; infer; dou
43. 想/考虑:think of…as; think about; consider; think over
44. 支持/反对:agree; disagree; accept; receive; refuse; turn down; be against; elect; vote for/ against
45. 花费:sth/doing sth+cost; sb+spend+ in doing sth; sb+afford +n/to
do sth ; It +takes/took some time/ money/energy to do sth; sb pay some
money for sth.
46. 省/存钱:se /se up; set aside; put away; spare no effort/ time
47. 参加:take part in; join /join in; attend; compete in/ for/against
48. 控告:accuse sb. of; charge sb. with
49. 救治/帮助: help /help out; se /rescue sb from sth.; treat; cure
sb. of sth; aid sb in doing sth / to do sth; help sb with sth assist sb
in doing sth
50. 逃避:run away; escape from; flee; hide
51. 阻止/禁止:prevent / keep/ stop sb. from doing sth; forbid doing sth.; ban; prohibit
52. 对付/处理:handle / do with / deal with /tackle /overcome sth ; solve; settle
53. 效仿:copy; imitate; learn from; learn
54. 爆发/发生:come about; hen to; take place; break out; burst out; go off; explode
55. 安装/装备:fasten; fix; set; equip; be armed with; be equipped with
56. 追求:pursuit; ran after; seek after; chase; catch up with; keep up with
57. 建议:advise; suggest; recommend; propose; urge; demand; persuade
58. 打算:plan / intend / design to do; be going to do /be about to do /will do
59. 似乎/好象:seem; ear; look like/ as if /as though
60. 开办/关闭:open; start; set up; close/close up; end; close down
名词类:
?
1期 vacation holiday spring break ask for lee be on holiday he two days off
2旅游 trip journey tour voyage trel tourist passenger go camping/picnicking/hiking
3职务人员 clerk secretary passer-by friend minister manager waitress guest host hostess
Assistant customer adult neighbor relative patient /vet staff crew nurse teacher
Conductor tailor sailor inventor gardener guard
4餐馆/定餐/就餐 inn restaurant kitchen menu bill order tip fork and knife
reserve /book table Taste delicious salad dash vegetables fruit tray
napkin
5诊所/看病/服药 clinic hospital take one’s temperature take
medicine/pills he a fever/flu/headache doctor physician surgeon
specialist patient
6车站/机场 airport on board miss the train/bus catch a train meet sb.
7身体部位 arm head hair brain waist back shoulder pulse wrist
8意志 will courage patience determination faith effort confidence ambition energy
9才能/品质 talent gift ability potential intelligent promising smart stupid careful proud
Strict honest cold serious easy-going learned knowledgeable
10优缺点 advantage disadvantage strength weakness
11目标 aim goal intention purpose belief faith
12方式 means method way manner roach
13身体素质 strong weak pale sick ill be well keep slim/ fit cut weight/put on weight
14图表 photo picture graph drawing table line/bar graph pie chart draw a sketch 划草图
15文章 reading translation essay poem paper novel/fiction article
magazine newspaper journal 日志 diary日记 Files form make a list of
16课堂class course lecture example reason message notes words phrase scholarship degree
Subject question trouble difficulty grades read comment marks
17 学校活动 match game activity hold a meeting /debate /speech/ ceremony
18建议/观点 advice suggestion idea proposal view recommandation
19气候/天气 climate weather storm windy cloudy rainy snow hot/cold/freezing/heat/warmth
20交通 by train/bus /boat bike on the train/bus /a bike drive a car ride a bike
give sb. a lift/ride
21习惯 habit custom get used to regular有规律的(形容词) practice惯例(名词)
22感觉 sight hearing touch smell sense
23情感 feeling emotion anger delight sadness sorrow
24 财富 money possessions wealth belongings fortunes treasure diamond be rich/well-off
25 运动比赛 on the playground on the track and filed pitch event game
match sports player Coach judge jogging weightlifting play
volleyball//
26衣服 clothes, cloth, clothing clothes统指各种衣服,谓语动词永远是复数, cloth指布,为不可数名词 clothing 服装的总称,指一件衣服用a piece of, an article of
27 incident, accident incident指小, accident指不幸的事故
形容词类
1人的各种感受
乐hy delighted to one’s joy pleased amused
悲 sad unhy painful bitter
平静 calm quiet silent/still peaceful
烦bother bored be fed up with
震惊 surprised astonished shocked /amazed
怕 in fear be frightened /scared /afraid
失望desperate disointed hopeless be depressed
满意be satisfied with /be content to do
生气 Annoyed angry disgusting burst into rage
2 表程度的副词类
narrowly/ Nearly/ almost hardly/ hard extremely/ very very/ quite
Accidently/ once in a while occasionaly/ once far / by far
Farther/ further better/ worse be well/ good however/ therefore/so/thus
高频词组大全
With the help of 在~~帮助下
under the leadership / care of 在~~领导/关心下
be strict with sb. 对~人要求严格
be strict in sth. 对~事要求严格
at present=at the present time 目前
for the present 暂时
in the sun/sunshine 在阳光下
under the sun 在世界上
lie in 位于~~之内
lie on 同~~接壤
lie to 位于~~之外
at least 至少
in the least 丝毫,一点
by name 名叫
in the name of 以~~名义
in the air 空中,在流传
on the air 播出
in the way 挡路,障碍,用~~方法
In a way 在某点上,在某种程度上
get one’s own way to do 随心所欲
give way 让步,屈服
ose one’s way 迷路
by the way 顺便说一下
on one’s way to 在去~~的路上
Come this way 这边走
at the corner 在拐角处(外角)
in the corner 在角落里(内角)
on the corner 在角落上(外角上)
judge by / from 根据~~来判断
judge for oneself 由某人自己来判断
at the end (of) 在~~结束时
at the beginning of 在~~开始时
at the back of 在~~背后,支持
at the age of ~~岁时
at the foot of 在~~脚下
at the bottom of 在~~底部
at the top of 在~~顶上
at/on the edge of 在~~边上
in the course of 在~~过程中
in the eyes of 从~~观点看来,在~~眼里
in the face of 面对~,尽管,纵使
in the middle of 在~中间
in the end =at last=finally 最后
on the eve of 在~~前夕
on the side of 在~~一边
after a time = after some time 过一段时间后
for a time = for some time 一时,有一段时间
behind time 迟到,过期
behind the times 落在时代后面
at no time 决不
in no time 立即,马上
at one time = once time 曾经
at a time = each time 每次
at times = sometimes 有时
at all times 经常,一直,始终
at the same time 同时
at the time 在~~的时候
by the time 到~~的时候
for a moment 一会儿
for the moment 暂时
at the moment 当时
the moment /minute /instance 正当~~一刹那
once or twice 一两次
more than once 不止一次
once more 重新,又
once upon a time 从前
once in a while 偶尔
1. 以break为中心的词组
break away from 脱离,逃离
break down 破坏,粉碎;瓦解;出故障,抛锚
break in 闯进,打断;使顺服
break into 闯入;强行进入;突然开始
break out 爆发,发生;准备使用;起锚
break the law 违反法律
break the record 破记录
break one’s promise 失言
break up 开垦,破碎;解散,分开,分解
2. 以catch为中心的词组
be caught doing 被发现做某事 be caught in the rain 淋雨
catch a bus/train 赶汽车/火车 catch a cold 伤风,感冒
catch one’s word 听懂某人的话 catch sight of 发现,瞥见
catch up with 赶上,追及,追上
3. 以come为中心的词组
come across 偶尔发现,想起;越过;偿付
come along 一道来,陪伴;进步,进展;出现
come at 达到,求得,得到;扑向,袭击
come back 回来;恢复,复原
come down 倒下;降落;跌落;病倒
come from 来自,起源于,从~~产生,生于
come in 进来,进入;流行起来;获名次
come into being 发生,产生,出现,形成
come into power 开始执政,当权,当选
come into use 开始使用,获得应用
come on 上演;开始;赶快;发展;登台;(问题)被提出
come to know 开始了解到
come out 出来,传出;出版;结果是;褪色;(秘密)泄露
come to 苏醒,复原;共计;达到;归结于
come to an end 终止,结束
come true 实现,成为现实;证实
come up 走近;上楼;长出,发芽
4. 以do为中心的词组
be done in 精疲力竭 be done with 完全结束
do a good deed 做一件好事 do away with 去掉,废除;弄死;浪费
do good to (=do sb. good) 有益于 do harm to (=do sb. good) 有害于
do its work 有效,有作用 do much 极有用
do wrong to 做错 do one’s best 尽某人最大努力
do one’s homework 做作业 do one’s utmost 尽力而为
do proud 足以使~~骄傲 do sb. justice 公平对待某人
do some cleaning (V+ing,etc.) 搞卫生 do sb. a for 帮助某人
do well in 学得不错,干得漂亮 do with 和~~相处,忍受,处理
do without 不需要,不用 do wonders 创造奇迹
he much to do with 和~~很有关系 he nothing to do with 与~~无关
he something to do with 和~~有关 in doing so=in so doing 这时,在这种情况下
That will do. 行了;够了
5. 以get为中心的词组
get about 徘徊,走动,旅行;流传 get above oneself 自视高傲
get accustomed to 习惯于,对~~习以为常 get across 度过,通过,横过;说服,使理解
get ahead of 胜过,超过 get along 前进,进步;同意;离去
get along with 与~~相处 get at 发现,了解;掌握;攻击
he got to do 不得不,必须 get away 离开,逃脱
get back 取回,回来;报复 get behind 落后;识破
get down 咽下;写下;使沮丧,使抑郁 get down to 认真对待,静下心来
get familiar with 熟悉 get hold of 获得,取得
get home 到家
get in 进入,陷入;牵涉
get off 送走;脱下(衣服);下车;
动身 get on 上车;穿上;进步,使前进;成功;相处
get upon with 进步;在~~方面获得成功
get one’s hand in 熟悉;习惯
get out of 由~~出来,从~~得出;避免;退休
get over 越过;恢复,痊愈;克服;完成
get ready for 为~~作准备
get rid of 除去,去掉;免除,摆脱
get through 到达,完成,通过;及格
get together 积聚,积累;商谈,取得一致意见
get up 起床,起立;研究,钻研;致力于;安排,组织
get used to 习惯于
6. 以give为中心的词组
be given to 沉溺于,癖好 give about 分配;传播
give and take 相互迁就 give away 赠送;牺牲;泄露;颁发
give back 归还 give cause 给予~~的理由
give ear to 侧耳倾听 give forth 发出,放出;发表
give in 屈服,让步,投降 give in to 同意,接受;向~~让步
give off 发出(烟,气味) give oneself out to be/as 自称为
give oneself up to 专心于;向~~自首 give out 分发,公布
give place to 让位于,被~~所替代 give rise to 引起,导致;使~~发生
give sb. to understand 通知某人 give up 放弃;停止
give way to 让步,退却;屈服于
7. 以look为中心的词组
look about 四下环顾;查看 look after 照顾,看管
look around 东张西望 look at 注视,着眼于
look back 回顾 look for 寻找;期待,期望
look down on 俯视;轻视 look forward to 盼望,期待
look into 窥视;调查;浏览 look like 看起来象
look on 旁观;面向 look out 向外看;注意;当心,堤防
look over 从上面看过去;检查 look through 透过~~看去;看穿;浏览
look up to 仰望,尊敬
8. 以make为中心的词组
be made from 由~~原料制成
be made of 由~~材料制成
be made up of 由~~组成
make a fool of 愚弄,欺骗
make a mistake 弄错
make a point of doing 强调;认为~~重要;决心,坚持
make advantages/use of 使用,利用
make after 追求,追赶
make believe 装
make certain 确信,把~~弄清楚
make contact with 接通,与~~接触,与~~联系
make for 去向,向~~前进;有利于
make friends with 和~~交友
make into 把~~制成,使~~转变为
make much of 重视;理解;赏识
make one’s mind on sth. 决定某事
make one’s own 当作自己的看待
make oneself at home 随便,别拘束
make out 填写;开支票;理解;辨认
make the best of 尽量利用;极为重视
make up 弥补,修理;赔偿,补偿;起草;编造;化装
make up to 接近,巴结;向~~求爱
make way for 为~~让路,让路于
on the make 急求成功;增加
9. 以put为中心的词组
put aside 把~~放在一边;搁置;排除
put away 把~~放好,把~~收拾;储藏;吃喝,吃掉
put back 把~~放回原处;驳回
put down 放下;镇压;制止;记下;削减;降落
put forward 提出;拨快;建议,推荐;提倡,倡议
put ~~ into 把~~放入;插入;翻译成
put off 推迟,延期;消除;推脱,推辞
put on 上演;穿上,带上
put up with 忍受,容忍
put one’s heart into 全神贯注,专心致志
put up 举起,挂起;提名,推荐;陈列
10. 以take为中心的词组
be taken aback 吃惊 take a seat 就坐
take a shower 淋浴,洗澡 take aim 瞄准,设立目标
take away 拿走,减去;夺去 take ~~ by surprise 出奇制胜
take one’s place 就坐,入坐
take care of 当心,注意;照顾;提防;谨慎;处理,对付;负责
take office 就职,上任
take ~~ for 把~当作
take off 脱去,除去;离开;起飞;模仿;起程;致死;复制,作副本;减弱
take one’s temperature 量体温
take part in 参与,参加
take it easy 别着急,慢慢来
take place = hen 发生,举行
take the place of 代替 take pride in 以~~为荣,对~~骄傲
take sb. by the arm 拉某人的胳膊
11. 以turn为中心的词组
give a new turn to 对~~予以新的看法
in one’s turn 轮到某人做某事
out of turn 不按次序的,不合适宜的
take one’s turn to do 轮到做
turn a blind eye to 对~~视而不见
turn against 背叛,取敌对态度
turn back 折回,往回走
turn down 折叠,翻下,驳回,拒绝考虑
turn into 走进;变成,变为
turn to ~~for help 求助于
turn off 关上(自来水,电器开关);解雇,辞退;避开(问题);制造;生产
turn on 打开(自来水,电器开关);反对;依靠,依赖,取决于
turn one’s attention to 把注意力转向
turn out 培养;证明是;制成;实际情况是
turn out to be 原来是,证明是,结果是
turn over a new leaf 翻开新的一页,重新开始,改过自新
turn (a)round 旋转,转过身来;改变意见;取新政策
turn to 变成;着手于
turn upside down 颠倒过来,翻过来;使陷入混乱
学习资料站《 中学新概念英语 》
高考英语语法的考点都有哪些
系动词
系动词又称联系动词,作为系动词,它本身有词义,但不能单独用作谓语,后边必须跟表语(也称补语),构成系表结构说明主语的状况、性质、特征等情况。
有些系动词又是实义动词,该动词表达实义时,有词义,可单独作谓语,例如:
He fell illyesterday.
(fall是系动词,后跟补足语,说明主语情况
He fell off theladder.
(fall是实义动词,单独作谓语。)
1)状态系动词
用来表示主语状态,只有be一词,例如:
He is a teacher.
(is与补足语一起说明主语的身份。)
2)持续系动词
用来表示主语继续或保持一种状况或态度,主要有keep, rest, remain, stay, lie, stand, 例如:
He always keptsilent at meeting.
This matter restsa mystery.
3)表像系动词
用来表示"看起来像"这一概念,主要有seem, ear, look, 例如:
He looks tired.
He seems (to be)very sad.
4)感官系动词
主要有feel, smell, sound, taste, 例如:
This kind of clothfeels very soft.
This flower smellsvery sweet.
5)变化系动词
表示主语变成什么样,有become, grow, turn, fall, get, go, come,run
He became madafter that.
She grew richwithin a short time.
6)终止系动词
表示主语已终止动作,主要有prove, trun out, 表达"证实","变成"之意,例如:
The rumor provedfalse.
The search proveddifficult. 搜查证实很难。
His plan turnedout a success. (turn out表终止性结果)
I、常见系动词错误及其成因:
(1)漏掉系动词
I afraid he won'tcome tomorrow .
( 2 )误用系动词
His hair changedgrey .(混淆了change 与turn,grow)
I.系动词分类:
一、根据系动词后所跟结构,分为两大类:完全系动词(其后只能跟表语的动词,如be)和半系动词(其后既可跟表语作系动词用法,也可跟宾语或状语作实义动词用,如look)
He looked sad atthe news.
(“看起来”,系动词用法)
He looks at aclever boy.
(“看着”,实义动词用法)
在英语中,某一动词是多义词,既有实义动词用法,又有系动词用法。常见的有:
listen, look ,touch ,hear,see ,sound ,feel, taste ,remain ,keep,stay, turn,become
二、根据系动词的意义,分为四类:
A.五大感官系动词 B.状态系动词
C.动态系动词 D.双谓语系动词
A.五大感官系动词,描述一种感官性质。由实义感官动词变化而来,都是半系动词
1.look“看起来像是”,后接adj.、n.、分词、介词短语、不定式等。
The girl bit herlips and looked thoughtful.
2.smell“闻起来”,后接adj.,分词。
The flowers smellsweet.
3.sound“听起来”,后接adj.,分词。
The music soundssweet.
4.taste“尝起来”,后接adj.,分词。
The les tastevery good.
5.feel①“摸起来,给……感觉”;②“觉得”,后接adj
The silk feelsvery soft.
You will feelbetter after a night’s sleep.
B.状态系动词:
1.be,“是”,完全系动词。
I am a student.
2.seem,“似乎,好像”,完全系动词。
They seem quitehy.
3.ear,“显得,看起来好像”,半系动词。
He eared tiredand sleepy.
It eared(tobe)a true story.
Now it ears tome that he may play an important part in settling the problem. (在我看来)
4.keep, “保持……的状态”,半系动词,后接adj或介词短语。
You’d better go to bed and keep warm.
5.remain,“仍是”,半系动词。
I remained silent.
6.stay“保持(某种状态)”,半系动词,后接adj.、过去分词。
The window stayedopen all the night.
7.prove “证明是”,半系动词,后接adj.,n.
The treatmentproved to be successful.
C.动态系动词:都属于半系动词,描述状态变化过程。
1.get“变成,变得……起来”,后可接形容词、分词、介词短语。
The days aregetting longer and longer.
The train didn’t get going again.
It’s nothing to get excited about.
My watch gets outof order.
2.fall“进入(某种状态),成为”,后常接以下形容词:
asleep, silent,ill, sick
The old man,unable to express himself, fell silent.
My father fell illand died.
3.grow“渐渐变得……起来,长得”
You will grow usedto it.
It’s growing warm.
4.turn“转变成(新的与原来完全不同的色彩或性质),变质(色)”。
Maple trees turnred in autumn.
It was cloudy thismorning, but fortunately it has turned fine.
He has turnedwriter.
(注意:此时writer之前无冠词a.)
5.go,“变成(某种坏的状态)”
The telephone hasgone dead.
The material hasgone a funny colour. (奇怪)
go之后常接的adj. 还有:bad, blind, wild, wrong, sour, hard, hungry,mad, red, with, anger, white, pale, blue, grey
6.become“变成,成为(好坏均可的情况)”
He became angrywith me.
It became dark.
They became goodfriends.
I becameinterested in drawing.
7.come,“变成为(已知的状态),证实为”,后接形容词或前缀un-的过去分词作表语,表示状态或情况的变化。
His wish to becomea pilot has come true.
If you look intothe matter, everything will come clear.
My shoelaces hecome undone.
后面常接的形容词还有:apart, dear(昂贵),natural,open, untied(松开)。
8.run,“变成”,后接adj.
The well has rundry.
The price ranhigh.
9.make,“达到某种状态[后接形容词],如sure, certain, merry, bold, free
We must makecertain of facts.
我们一定要弄清事实。
The Children makefree with the les.
孩子们随便吃苹果。
D.双谓语系动词
此类系动词既有系动词的功能,后接表语,又保留原实义动词本身的含义。例如:
The run rose red. 太阳升起红艳艳。
She stopped andstood quite still.
The book lay openon the table.
The snow lay thickon the ground.
He marriedyoung.
The window blew open.
III.系动词用法应注意的八个问题
1.系动词的进行时态应分情况讨论
一般,状态系动词无进行时态,而动态系动词有进行时态。但在某些情况下,状态系动词也有进行时态,表示两个用途:
(1)表示一种短暂的、反常的状态。如:
He is being kind.
他装出和蔼可亲的样子(一时而不能持久的性质)
(2)表示一种探询口气,使语言客气、生动、亲切。例如:
I hope you arekeeping well.
(语气委婉)
Are you feelingany better?
(语气亲切)
试比较:
Your hand feelscold.
你的手摸起来冰凉(无意识的静态性质)
不可以说:
Your hand isfeeling cold.(×)
The doctor isfeeling her pulse.
医生正在给她把脉(有意识的动态动作)
The soup tastesgood.
这汤的味道不错(静态性质,无进行时)
The cook istasting the soup.厨师在尝汤的味道。(动态动作,有进行时)
总之,系动词有无进行时态应随系动词的意义或其语境变化而变化。在概述某一动词的进行时态时,不能笼统地说feel,smell无进行时,应指出其意义及其语用环境。以smell为例
①smell作“嗅觉”的能力时,虽是实义动词,但指的是一种性质的存在状态不能用于进行时态,常与can, could, be able to连用。
The camels cansmell the water a mile off.
骆驼能嗅出一英里外有水。
②指“嗅、闻”的动作时,实义动词,可用于进行时态。
The girl issmelling the flower.
③smell指“含有……气味”,“发出……气味”等事物性质时,半系动词,无进行时态。
The dinner smellsgood.
2.系动词的时态与形容词的比较级连用的问题
某些含有变化意义的动态系动词如get, become, grow, turn等的进行时态可与形容词的比较级连用,表示渐进过程,其意思是“越来越……”。
He is growingtaller and taller.
Our life isgetting better and better.
The things aregetting worse.
3.所有半系动词的被动语态要分情况讨论
某动词在作系动词用时,无被动语态,而作实义动词用时,才有被动语态
不能说: The le is tasted good.
(因为taste此时是系动词,“尝起来”之意,指的是苹果的性质,无被动语态)
但可以说: The le is tasted by me.
(taste此时指“尝一尝”这一动作,有被动语态)
因此要注意半系动词在具体的语言环境中到底是系动词用法还是实义动词用法
4.瞬间动态系动词能否与时间段连用的问题
某些表示瞬间意义的系动词不能与“for+时间段,since+时间点,how long until+时间,by + 时间,so far”直接连用
①不能说:
He has become ateacher for 2 years.
应改为:
He has been ateacher for 2 years.
②不能说:He has turned writer since 3 years ago.
应改为:He has been a write since 3 years ago.
或It is two years since he turned writer.
③不能说:He got angry until his child came backhome.
应改为:He didn’t getangry until his child came back home.
5.系动词能接几种表语(从句)
系动词除了接adj.\n.\介词短语,某些adv.以外,还可接以下几种表语形式:
①能接as if/as though表语从句的系动词有:look,smell,sound,feel;ear(显得),seem(似乎)
It looks as if weare going to he snow.
He looked as if hehad just stepped out of my book of fairy tales.
It seems as if it werespring already.
②可用于“It+系动词+that从句”结构的有:seem, ear, 不可用be, look
It seemed that hehad made some serious mistakes in his work.
It eared thathe was talking to himself.
③能用不定式作表语的系动词有:be, seem, get, look, ear, prove, grow.
Her job is to lookafter the children.
He looks to be ayoung girl of twenty.
④能与there连用的系动词有:be,ear, seem.
There eared tobe only one room.
There seems(tobe)no need to go.
6.能用两种否定形式的系动词有两个:seem, ear.
It doesn’t seem that we can get our money back.
= It seems that wecan’t get our money back.
He seems not to beher father.
= He doesn’t seem to be her father.
The baby doesn’t ear to be awake.
= The baby earsnot to be awake.
7、几组易混系动词的区别
系动词的区别主要从两个方面作比较,一是其意义,二是其结构。
1)get, become, go, turn, grow“变成”
get:“变得”口语。后接形容词、现在分词、过去分词、介词短语、不定式作表语,但不能与名词直接连用。
become:“变成,成为(好坏情况均可)。”后接形容词、名词、过去分词作表语,不能与不定式连用。
go:“变成(某种由好到坏的情况)”,后接形容词、过去分词、名词作表语。
Turn:“转变成”强调与原来不同的、新的变化,如变质、变色等。后接形容词、不带冠词的名词作表语,后不接不定式。
grow:“逐渐变得……”,强调其变化过程。后接形容词、分词、不定式,不可直接跟名词。
2)look, seem, ear“好像”
三者作系动词时在意义上的区别:
look:“好像,看起来”,一般用于非正式场合,侧重指从本身外表特征上由视觉得到的印象。
seem :“似乎,好像”,指说话人内心的估计与判断,有一定依据,接近于实际情况。
ear:“显得,好像”,常用于正式文体中,指某事物或人给他人的表面印象,有时含有实质上并非如此之意。
He looks like hisfather. (指其长相看起来相像)
He seems like hisfather. (指说话人从个性方面得到的判断)
He ears likehis father.(指他的外貌、衣着给他人的印象)
3)keep, remain, stay“保持……状态”
①keep作系动词时,“保持……状态”,后接adj.或介词短语:alive,awake,cheerful,silent,dry,well,fit,fine,close,clean,hy
He you kept wellall these years?
I hope it willkeep fine.
In order to keepfit, all students go in for sports.
We’d better keep in touch.
②remain,系动词“仍然存在……状态”,后接adj.、过去分词、名词或介词短语,强调某种状态前后无变化。
The door remainedclosed.
门仍然关着。
Your room remainslike this.
你的房间依旧是这样子。
③stay,作系动词用时“保持……状态”,后接形容词、分词。
That fellow stayedsingle.
那个小伙子仍保持单身。
It’s easy to stay hidden.
躲起来很容易。
后常接的形容词有:calm, clean, fresh, healthy, young, open,awake, warm, fine, 常可与keep互换。如:
Stay/keepcalm(clean, fine, healthy, awake等)
①What you he said_______.
A.is soundedinteresting
B.soundsinteresting
C.soundinterested
D.listensinterested
②The class begins. Please keep________.
A.silent B.silence
C.the silence D.silently
③Look! Several people in the crowdseemed_______.
A.to be fighting B.to hefought
C.being fought D.hingfought
④How _____the song she sings sounds! I henever ______a better voice.
A.beautifully, sounded
B.beautiful, sounded
C.sweet, listened to
D.sweet, heard
⑤Her feeling about the marriage ______ratherstrange.
A.is looked B.is seemed
C.seems D.iseared
⑥John _____driver since two months ago.
A.became a B.has becomea
C.has turned D.has been a
⑦The ice_____ thick on the river.
A.is lain
B.lay
C.laid
D.lie
高考英语语法有哪些
高中语法主要有主谓一致、冠词、代词、连词、介词、动词短语、情态动词、时态语态、虚拟语气、非谓语动词、形容词、副词、名词、动词、从句等。
高考英语语法考点
一、定语从考点
1.which引导的代表整个主句内容的非限制性定语从句which引导非限制性定语从句时可代表主句内容,前面有逗号与主句隔开。
例句:The CCTV’s 2010 Entertainment Party was successfullyheld on the evening of February 13th,2010, which wasanother great encouragement to all the Chinese.中央电视台2010年春节文娱晚会于2010年2月13日晚成功举行,这对全体中国人民来说又是一个巨大的鼓舞。
2.特定词汇+of whom ,which引导的非限制性定语从句介词(包括复杂介词),数词(包括数量代词)及其它含局部与整体关系的特定词~E+of whom(指人)/which(指物)可以引导非限制性定语从句,此时前面不可加and,but等连词,该结构也可改为of whom /which+特定词汇引导定语从句。
例句:Our English teacher has three daughters,all of whom /ofwhom all are considerate.
我们的英语老师有三个女儿,个个都很善解人意
3.由when.where引导的先行词隐蔽度比较高的定语从句历年的高考考查实践表明,增加定语从句难度的手段之一是增加先行词的隐蔽度,如用point,case,situation等抽象的地点名词做先行词,当其在定语从句中做地点状语时用where引导定语从句的判断难度会增加,用occasion,period等表示抽象时间的名词做先行词,当其在定语从句中做时间状语时用when引导定语从句的判别难度也会增加。
例句:I’m sorry that I can’t think out a situation where thiskind of deion is used.
对不起我想不出这种描绘被使用的场合。
二、名词性从句考点
1.what引导的名词性从句
what可引导名词性从句,表示“. ·-的内容(人、时间、地点、价格、速度、方式等)”。The Great Wall of China is what I most want to visit.长城是我最想参观的地方。
2. that引导的同位语从句
that可引导同位语从句,说明被修饰名词的内容。
例句:Word hascome that the sports meeting will be put of.
有消息说运动会将被推迟。
3.whatever.whoever引导的名词性从句 whatever和whoever可引导名词Jl生从句,前者表示“无论什么 ,后者表示“不管谁 。
例句:You can give the book to whoever you think needs it.
你可以把这本书给任何你认为需要这本书的人。
4.whether,if引导的名词性从句
if只可引导宾语从句且不能和or not连用。whether可引导各种名词性从句且可和or not连用。
例句:When shall we discuss the question whether we will hea picnic next week?
我们什么时候讨论下周是否搞一次野餐的问题?
三、状语从句考点
1.where引导的地点状语从句
where可引导地点状语从句,表示“在..的地方 。0ur school lies where there is a small river.我们学校位于有一条小河的地方。
2.before引导的时间状语从句
before引导时间状语从句时可表示“在..之前,尚未来得及,趁 。
例句:Thenaughty boy had run away before I could call him tostop.
我还没有来得及叫住他,这个调皮男孩就跑开了。
3.unless.as/so long as引导的条件状语从句
unless,as/so long as可弓I导条件状语从句,前者表示。除非 ,后者表示“只要 。
例句:As/So long as you treat them truly,you can win overtheir respect.
只要你真诚地对待他们,你会赢得他们的尊敬。
4 . so that.in case引导的目的状语从句
so that,in ease可引导目的状语从旬,前者表示“以便”,后者表示“以免 。
例句:Please close all the doors and windows in ease it willrain.
请关上所有门窗,以防天会下雨。
5.while引导的让步状语从句
while可引导让步状语从句,表示“尽管”。
例句:While this problem is very difficult,it is very important.
尽管这道题很难,却很重要。
四、情态动词考点
1.推测性情态动词用法
may(可许,可能),might(可许,可能),must(一定,必定),can(或许,可能)均有推测性用法,其中might可能性最小,must可能性最大。may,might,must常用于肯定句,may,might用于否定句可表示“可能不 ,can常用于否定句和疑问句,用于否定句表示 不可能 。
例句:— — Can the man standing there be OUY physics teacher?
— — No.he can’t be our physics teacher.
— — 站在那边的那个人可能是我们的物理老师吗?
— — 不,不可能。
2.should的用法
should常表示“应该”,但可置于句首用于条件状语从句(省去if),表示。万一 ,还可表示 竟然
例句:Should you see the thiel,try to catch him.如果你见到小偷,尽量捉住他。
3.may,must,earl’t,should (shouldn’t),ought to(oughtn’tto).needn’t的完成式用法m he done表示“可能已经做了某事 ,must he done表示“一定已经做了某事”,can’t he done表示“不可能已经做了某事”,should/ought to he done表示“本来应该做某事但实际未做 ,shouldn’t/oughtn’t to he done表示 本来不应该做某事但实际已做”,Ileedn’t he done表示“本来没有必要做某事但实际已做”。
例句:Our Chinese teacher isn’t in her offlee,so she may /might/must he gone home.
我们的语文老师不在办公室,所以她可能/-~定回家了。
五、倒装句型考点
1.完全倒装句型考点
地点状语置于句首时需要使用完全倒装句型,将动词直接提前。
例句:At the back of our school stands a high tower.
我们学校后面矗立着一座高塔。
SO(肯定句中表示“也”),neither,IOF(否定旬中表示“也”),80.that. (引导结果状语从句)j only(不修饰主句),no[only.but also. (不连接主语,连接两个分旬时第一个分旬倒装,第二个分句不倒装),not until,Never,hardly,little,hardly.when., SO SO01qe/"than,not a,nowhere,in no ease等词或短语置于句首时应使用不完全倒装句型。
例句:Only then did we realize the harm of pollution.
只有在那时我们才意识到污染的危害。
2.as引导的特殊倒装句型
as引导让步状语从句时可将表语、动词、副词提前,将as紧随其后。如果表语为单数可数名词,提前时应去掉不定冠词。
例句:Weak as she was,she still went on working.
尽管她身体虚弱,仍继续工作。
六、虚拟语气考点
1.与过去事实相反的if虚拟条件状语从句与过去事实相反时,从句动词用had done,主句动词用would,could,should,might he done,当从句动词含有were,had,could,should时可将其提至句首将if省略。
例句:Had I known it at that time,I would he told you.
如果那时我知道这件事一定告诉了你。
2.混合虚拟条件从句
如果if虚拟条件状语主从句时态不一致,应根据各自所体现的时间关系加以适当的调整,用不同的动词形式。
例句:If she had told me her telephone number yesterday,Icould phone her now.
如果她昨天把她的电话号码告诉了我,我现在就可以给她打电话了。
3.with.without.but for引导的含蓄虚拟条件从句with,without,but for可取代if引导含蓄虚拟条件从句。
例句:With your help,I could he made more achievements.
如果得到你的帮助,我一定会取得更多成就。
4.wish引导的表示过去主观愿望的宾语从句
wish引导宾语从句时如果表示过去的主观愿望,从句动词应用had done或could he done。
例句:I wish I had /could he watched that basketball matchyesterdayafternoon.
我希望我昨天下午看了那场篮球赛。
5.insist,suggest引导的宾语从句
insist,suggest接宾语从若表示建议应用虚拟语气,动词形式为(should)do,但如果insist表示 坚持认为,固执己见 ,suggest表示。表明、暗示 ,所在宾语从句应用陈述语气。
例句:Thedoctor insisted that the patient was seriously ill and(should)be 0Dcrated 0n at once. 医生坚持认为病人病得很严重,建议其立即做手术。
七、不定式考点
1.不定式做目的状语
不定式可做目的状语,如果对其强调可将其提至句首,此时应注意人称一致。
为了及时赶到那里,她将自行车骑得很快。
误:T0 get there in time.her bike waS ridden fast.
正:To get there in time.she rode her bike fast.
2.不定式做结果状语
不定式可做结果状语,强调出乎意料的动作,此时前面可加onlyo
例句:I went to see her to find her absent.
我去看她结果发现她不在家。
3.不定式的复杂形式
不定式除有一般式外,还有否定式not to do,进行式to bedoing、完成式to he done、被动式to be done、完成被动式tohe beendone等复杂形式。
例句;All the employees worked hard not to be fired.
为了不被解雇,所有的员工努力工作。
4.不定式独立主格结构
with+名词+不定式可构成独立主格结构做状语,表示未来的动作。
例句:Witha lot of work to do,I can’t help you at present.
因为有许多工作要做,我现在不能帮助你。
八、V—ing形式考点
1.V—ing形式做宾语
excuse. f0r. ,can’t help,suggest,include,insist on,keep on, consider, finish, practice, put off, postpone, delay,miss,oid,give up,imagine,feel like,enjoy,risk,mind,reciate,stand,escape等词后面只能接V—ing形式做宾语。remember 得曾做某事),forget(忘了曾做某事),mean(意谓着),try(尝试),regret (后悔),go on (继续做同一件事),stop(停止做某事),need(主语需要被..)等词表示括号内的含义时也应接v—ing形式做宾语。
例句:The hare was lucky enough to he oided being caught.
这只野兔很,错过了被捉住。
2.V—ing形式做定语
V—ing形式做定语可表示被修饰名词的的用途和性质,也可表示正在进行的动作。
例句:The great noise comes from the building being built now.
这巨大的噪音来自正在被建的楼房。
3.V—ing形式做状语
V—ing形式做状语常表示动作正在进行,此时应注意它的逻辑主语为主句主语。
例句:Holding a book in his hand,he came into the room.
他手里拿着一本书走进了房间。
4. V—ing形式做宾语补足语
V—ing形式做宾语补足语也表示动作正在进行。
例句:WhenI came to the five~ide.I f0und girl struggling inthe water.
来到河边时我看见一个女孩在水中挣扎。
5. V—ing形式独立主格结构
with+名词+V—ing形式可构成独立主格结构做状语,表示正在进行的动作。
例句:With the water still rising,the villages couldn’t return totheir village.
因为水位还在上涨,村民们无法回到村里。
6.V—ing形式复杂形式
V—ing形式除有一般式外还有完成式hing done,被动式being done,完成被动式hing been done,否定式not doing,完成否定式not hing done,完成被动式的否定式not hingbeen done。
例句:Hingsaid goodbye to each other, the children wenthome.
彼此说了再见之后,孩子们回家了。
九、过去分词考点猜想
1.过去分词做状语
过去分词做状语常表示被动的动作,也可因来自系表结构而表示主动的动作。
例句:Caught in a hey rain,the girl was all wet.
因为被浇了一场大雨,这女孩浑身湿透了。
2.过去分词独立主格结构
with+名词+过去分词可构成独立主格结构做状语,表示被动的动作。
例句:With his homework finished, the boy went out to getrelaxed.
因为家庭作业完成了,这个男孩出去放松了一下。
高考需要掌握的不及物动词有哪些(英语)
一.非谓语动词
一.不定式:
一)不定式的常考形式:
1) 一般形式:He decided to work harder in order to catch up with the others.
被动形式: He preferred to be assigned some heier work to do.
语法功能: 表示与谓语动词同步发生
2) 完成形式:He pretended not to he seen me.
被动形式:The book is said to he been translated into many languages.
语法功能:表示发生在谓语动词之前
二)不定式常考的考点:
1)不定式做定语----将要发生
2)不定式做状语----目的
3)不定式充当名词功能---To see is to believe.
三)不定式的省略
1)感官动词 see, watch, observe, notice, look at, hear, listen to, smell, taste, feel
+ do 表示动作的完整性,真实性;
+ doing 表示动作的连续性,进行性
I saw him work in the garden yesterday.
昨天我看见他在花园里干活了。(强调"我看见了"这个事实)
I saw him working in the garden yesterday.
昨天我见他正在花园里干活。(强调"我见他正干活"这个动作)
" 感官动词后面接形容词而不是副词:The cake tastes good; It feels comfortable.
2) 使役动词 he bid make let 等词后不定式要省略但同1)一样被动以后要还原to
I 'd like to he John do it.
I he my package weighed.
Paul doesn't he to be made to learn.
3) help help sb do help sb to do help do help to do
四)有些动词后只跟不定式如:
want,wish,hope,manage,promise,refuse,pretend,plan, offer,decide,agree,expect allow sb to do, cause sb to do , permit sb to do, enable sb to do
force sb to do. be more likely to do love to do warn sb to do be able to do
be ambitious to do. begin to do . start to do
We agreed _______ here,but so far she hasn't turned up yet.(NMET
1995)
A.hing met B.meeting C.to meet D.to he met (Key:C)
五) 有的时候to后面要接-ing形式
accustom (oneself) to; be accustomed to; face up to; in addition to; look forward to; object to; be reduced to; resign oneself to; be resigned to; resort to; sink to; be used to; be alternative to; be close/closeness to; be dedication/dedicated to; be opposition/opposed to; be similarity/similar to.
三、need/want 后的-ing形式具有被动的意思。其中,want不太常用。
He needs (a lot of) encouraging.
二. 动名词: 具有动作性特征的名词
1)是名词 seeing is believing
2)具有动词性特征可以带宾语 starving troops is necessary.
一)动名词的形式:
一般形式:I don't like you smoking.
完成形式:I regret not hing taken your advice.
被动形式:This question is far from being settled.
二) 动名词常考的点
1)动名词做主语谓语动词为单数
2)在动名词和不定式中,做为介词的宾语是动名词
3)动名词的否定直接在其前加否定词,通过代词的宾格或所有格形式给出逻辑主语.
I would reciate_______ back this afternoon.(MET 1992)
A.you to call B.you call C.you calling D.you're calling(Key:C your calling 也对)
I regret not hing taken your advice.
4)有些词后只能接动名词
admit; reciate; oid; celebrate; consider; contemplate; defer; delay; deny; detest; discontinue; dislike; dispute; enjoy; it entails; escape; excuse; explain; fancy; feel like; finish; forgive; can't help; hinder; imagine; it involves; keep; it means; mention; mind; miss; it necessitates; pardon; postpone; practice; prevent; recall; report; resent; resist; risk; suggest; understand...
另外还有一些接-ing形式的常用说法:
it's no good; it's no/little/hardly any/ use; it's not/hardly/scarcely use; it's worthwhile; spend money/time; there's no; there's no point in; there's nothing worse than; what's the use/point...
5有些词后加不定式和动名词均可
remember, forget, try, stop, go on, cease, mean后面用不定式和-ing形式,意义截然不容。
I remembered to post the letters. (指未来/过去未来的动作)
I remembered posting/hing posting the letters (我记得这个动作)
forgot remember的用法类似。
I regret to inform you that… 我很遗憾地通知你…
I regretted hing left the firm after twenty years. 为了"二十年前的离开"而遗憾。
try to 努力 You really must try to overcome your shyness.
try -ing 试验 Try practicing five hours a day.
I mean to go, but my father would not allow me to. [打算、想]我想去,但我父亲不让我去。
To raise wage means increasing purchasing power. [意味着]赠加工资意味着增加购买力。
prefer的用法:
我宁愿在这里等。
3 分词:
现在分词主动进行,过去分词被动状态
现在分词的形式:
1)一般式: Do you see the man talking to the dean(主任)? (与谓语动词同步发生)
2)完成形式:Not hing made adequate preparations, they failed. (发生谓语动词之前)
3)完成被动形式:Hing been adapted, the script seems perfect.( 发生谓语动词之前且表示被动)
过去分词
1) 过去分词表示被动:Fight no battle unprepared.
2)过去分词的进行形式:You'll find the topic being discussed everywhere. (强调正在被做)
这三种非谓语动词,都可以构成复合结构,非谓语动词所修饰的成分是这些非谓语动词的逻辑主语。他们之间的一致关系--主动还是被动,往往就是考点。独立主格结构中,要注意的是分词与他前面的逻辑主语之间的主动被动的关系。
二:虚拟语气和情态动词
情态动词的基本用法及其区别
最近几年高考试题中常常借助语境来考查情态动词的基本用法及其区别,因此在平时学习时准确理解和掌握情态动词的基本用法十分重要。情态动词的用法复杂多变,在高考试题中,命题者常常利用语境和句子之间意义上的细微差别来考查学生对情态动词的理解和掌握。对于情态动词,除了要求考生能够准确掌握它们的基本用法外,还要充分利用高考试题所设置的语境来分析句子之间所体现的特殊关系。下面就近几年来高考试题中出现的情态动词的考点进行归纳分析,以便同学们复习掌握。
一、用"情态动词+he +done"结构表示对过去动作的推测,高考试题中常用过去时态或过去的时间状语给以暗示。情态动词的这一用法可以用 "对立统一"来概括。
1.当试题的前句和后句在动作和意义上相互补充说明,且整个句意在动作和时间上是一个整体时,我们可用"统一"关系来解决这样的试题。常见的结构有:
must he done:
表示对过去动作的肯定推测,常译作"一定做了……",只能用于肯定句中。其否定形式为can't/couldn't he done?
疑问式为Can/Could...he done?。
could /might he done:表示对过去发生的动作的可能性推测,常译作"可能做了……"。如:
1) My sister met him at the Grand Theater yesterday afternoon, so he
_____ your lecture. ?(上海 2000)
A. couldn't he attended
B. needn't he attended
C. mustn't he attended
D. shouldn't he attended
本题选A。
2) Jack ____ yet, otherwise he would he telephoned me. (上海'
A. mustn't he arrived
B. shouldn't he arrived
C. can't he arrived
D. need not he arrived (C)
2.当试题的前后句在动作和意义上构成转折关系时,常借助"but, however, instead"等词来表示过去的动作与客观事实不符,这时我们就可以用"对立"关系来解决这样的试题。这种结构常见的有:
should he done / ought to he done:表示过去本应该做某事而实际上没有做。
should not he done / ought not to he done:表示过去本不应该做某事但事实上却做了。
由句中的连词but可知前后句之间是对立关系,分析题意可知本题应选C。
二、考查情态动词基本用法之间的比较和辨析。最近几年高考试题中常借助具体的语境来考查考生对那些最常见的情态动词的基本用法的理解和掌握,因此在做这样的试题时应认真分析语境中所含的实际意义,并结合情态动词的基本含义和用法做出正确的选择。
虚拟语气
" 最自然的虚拟状态:由should/would+原型时态(不含时间只含状态)
本质上是过去将来时:即,时间固定在过去将来,状态不同:一般、进行、完成、完成进行。
这时"虚拟语气"的产生往往是因为我们要表达"本来应该……"(而现在却还没有……)
(本来可以……,本来能……)
一些常见的句型中,就会出现这种虚拟语气,而处于从句之中,should 常常被省略掉
o suggest, advise, propose, recommend, plan;
o demand, order, direct, arrange, command, decide;
o require, request;
o think, expect, believe, insist, suspect.
由于他们的含义中包含"建议,设,应该"这类的含义,所以,由他们引起的从句中,就会包含有should+原型时态构成的虚拟语气。
这些动词(以及他们的名次形式,分词形式)引起的从句还有其他的变形
主语从句,表语从句,同位语从句
It's suggested that…
My suggestion is that…
The only suggestion that...
The only suggestion I can give you now is that…
一些形容词引起的表语从句中,也会有同样的情况
important; necessary; essential
It's natural ; strange; incredible that
a pity; a shame; no wonder
? 由lest, for fear that, in case 引起的从句中多使用should
" 表达与事实相反
1. 与现在相反:使用[过去时]:
I wish I were not here! (一般现在'一般过去)
Suppose we were not here.
He loved me as if I were his own son. (一般现在'一般过去)
Hope I weren't always losing things! (现在进行'过去进行)
If only/If I hadn't been there! (现在完成'过去完成)
What if I hadn't been waiting right here! (现在完成进行'过去完成进行)
常考句型:It's (high) time (that)…; would rather (that)…
这两个从句,只能表达对现在的看法,所以,从句中只有一般过去时。
2. 与过去相反:过去完成时;
3. 与将来相反?将来的事情没有发生,所以只能推测且实现可能很小
I wish he could not smoke any more.
不过,由于可以用be to表示将来;所以,虚拟语气中经常出现were to;也是CET-4的常考语法点。
" 虚拟条件句
o if 部分,做一个与事实相反的设(所以只有一般过去和过去完成)
o 主句部分,这是表示基于这个设的推测,一般使用情态动词would,少数情况下使用could/might/should。
o 注意:两个部分之间,是有逻辑关系,而在两部分的谓语动词时态上,没有必然的联系。
" 注意,虚拟条件句中的if可以省略,造成were/had提前,产生倒装。
" 隐含的非真实条件 :由特殊的词给出条件: with, without, in , but for, otherwise, or
How could I be hy without you? In his shoes, I would kill myself.
But for the storm, we would he arrived.
三、一致关系
一)主谓一致
1. 主谓一致(与插入语无关)
1主谓的分隔原则:主谓之间可以用定语从句或者省略的定语从句分隔。
2定语从句中的主谓一致:
3随前一致:
n. + together with n2
as well as
including
along with
with / of
accompanied with / by
4就近原则:n1 or n2 +v(就近原则)
either n1 or n2
5可数n1 and 可数n2+v(pl)
不可数n1 and 不可数n2+v(pl)
例外:war and peace is… war and peace是一个整体
但是如果主语表示的是同一个概念,同一人,同一事的时候,谓语动词用单数,这种结构的特征是and连接的两个词只有一个冠词。
The iron and steel industry is very important to our country.
The head master and mathematical teacher is coming.
The head master and the mathematical teacher are coming.
类似的还有:law and order bread and
butter black and white
To love and to be loved is …
A lawyer and a teacher are…
A lawyer and teacher is …
6随后原则:not A but B / not only A but also B+v.(与B一致)
7百分比结构:most , half , rest , some , majority , one+persent
of+n1+v.(由n1决定
8倒装结构的主谓一致:
a)There be +n 由名词决定动词
b)Among , between等介词位于句首引起倒装结构:
Among / Between …+系动词+n. (由名词决定动词)
9The+adj的主谓一致:
a)当表示"一类人",
b)当表示某一抽象概念时
The good is always attractive.
10 To do/doing/主从+vs
*More than one+n
many a +n.
a day or two
二)、倒装
1 全部倒装
是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用与一般现在时和一般过去时。常见的结构有:Up went the plane = the plane went up.
1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, come, go, lie, run。
2) 表示运动方向的副词(back, down, off, up)或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。
注意:1) 上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能倒装。Here he comes. Away they went. 2) 谓语动词是be的时候,不能倒装。 Here it is. Here you are.
3) 形容词短语/分词短语位于句首,引起倒装
*typical of characteristic of
*coinciding with + n
4) 表示地点范围的介词短语位于句首,谓语动词为系动词,一定引起倒装
In…(表语)+系动词+主,主同。
*在倒装句型答案中不能出现there
*常考介词要倒装:among between in at beneath
常考的系动词:be lie exist remain rest
部分倒装
1. 否定 adv 位于句首,引起倒装:not only, not until, hardly, scarcely,
seldom, rarely, no sooner…than
1) not until + 时间 + 主谓倒装,not until + 句子+主谓倒装
2) only+状语位于句首
only +ad. eg: recently
prep.短短语 eg: in recently years
从句 eg: when clause
only一个词本身不倒装
3) 在比较级结构中,than后面可以倒装,也可以不倒装。
部分倒装是指将谓语的一部分如助动词或情态倒装至主语之前。如果句中的谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则需添加助动词do, does或did,并将其置于主语之前。
? 1) Neither, nor, so 表示前面句子的共同否定或者肯定,产生倒装,一般主动词提前,谓语动词的其他部分就
4) as / though引导的让步从句必须将表语或状语提前 (形容词, 副词, 分词, 实义动词提前)。
as〔让步〕虽然,尽管〔词序倒装。语气比 though 强〕。
Successful as he is, he is not proud. 他虽成功,却不骄傲。
Women as she is, she's every bre.
Try hard as he will, he never seems able to do the work satisfactorily.
注意:A) 句首名词不能带任何冠词。B) 句首是实义动词, 其他助动词放在主语后。如果实义动词有宾语和状语, 随实义动词一起放在主语之前。
5) 其他部分倒装
a) so… that 句型中的so; such… that句型中的such位于句首时,需倒装。
So frightened was he that he did not dare to move an inch.
b) 在某些表示祝愿的句型中:May you all be hy.
c) 在虚拟语气条件句中从句谓语动词有were, had, should等词,可将if 省略,把 were, had, should 移到主语之前,取部分倒装。Were I you, I would try it again.
四、复合句
从句可分为:
? 名词性从句' 主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句
? 形容词性从句'定语从句
? 副词性从句'状语从句
" 常考的关系代词:that; which; who/whom/whose; where; when; what; as。
" 常见的同位语从句现行词(that之前的抽象名词):fact, idea, news, hope, conclusion, evidence, opinion, problem, thought, understanding…
" 常用的引导词
o 时间状语从句:while; when; before; whenever; as; after; till; until; since; once; ever since; as/so long as; as soon as; no sooner… than; hardly… when; scarcely/barely… when; the moment/minute/instant; on (the point of) doing…
o 地点状语从句:where; wherever
o 原因状语从句:because; since; as; seeing that; considering that; now that; in that; for fear that; lest; owing to the fact that; because of the fact that; due to the fact that…
o 方式状语从句:as; as if; as though; how; se that…
o 比较状语从句:as; than; as… as; not so… as; hardly… than;
o 结果状语从句:so that; so… that; such… that; so as to…
o 条件状语从句:if; unless; in case; so long as; so far as; provided/providing/that; supposing; granted/granting that…; giving that…
o 让步状语从句:though; although; even if; even though; whether; as; however; no matter (what, how, when); for all that; in spite of the fact that; granted that; regardless of the fact that…
o 目的状语从句:that; so that; in order that; lest; for the fear that; in case…
定语从句:
which 引导的定语从句结构
1)which是关系代词,which后面应该加缺主语或者宾语的句子,
在这个句子中,which要作成分,作主语或者宾语
2)in which+完整的句子
which在定语从句中作in的宾语,所以不能作后面句子的主语
3)名词+of which+谓语动词
of which来修饰名词,名词在定语从句中作主语,所以后面直接跟谓语动词
I he five books three of which are borrowed from Mary.
4)介词+ which +to do 其功能相当于定语从句。
The key with which to open the door is lost.
5)定语从句的省略结构:
1. 如果that / which在定从中作 宾语,可以省略.
sub+vt+n+(which / that)+sub+vt
→s+vt+n+s+v
s+vt+n1+n2+vt
*当做题时,若发现两个名词在一起,但是似乎连不上,则一定省略that /
which,则动词为vt,做谓语。
6)定从的特殊省略
the way (in which) + 句子
the reason (why that)+句子 均为完整句
the time (that / when)+句子
I do remember the first time (that省) I ever heard the sweetest voice in the world.
By the time省that+句子,句子。
7)定从的主系省略(主+系可同时省)
即:which be , who be , that be可同时省
状语从句省略结构
这种省略从句主语的方式理论上需要满足以下两个条件:
第一、特定的状语从句引导词:although though even though when while if as
第二、从句主语和主句主语必须保持一致;
第三、从句的谓语必须是be动词,主语和be动词同进同出,比如上面的they和are要么同时省略,要么同时保留。
高考英语插入语及插入句的用法
在NMET中,插入语屡见不鲜,由于插入语通常与句中其它成分没有语法上的关系,因此给考生的理解带来一定困难。插入语多半用逗号与句子隔开,用来表示说话者对句子所表达的意思的态度。插入语可能是一个词、一个短语或一个句子。
一、常用做插入语的副词
indeed的确, surely无疑, however然而, obviously显然, frankly坦率地说, naturally自然, luckily (或hily) for sb.算某人, fortunately幸好, strangely奇怪, hone stly真的, briefly简单地说等。
1. Surely, she won?t go to China Telecom with you.
当然她不会和你一起去中国电信。
2. Strangely, he has not been to China Unicom. Still more strangely, he has not called me.
奇怪,他未来过中国联通。更奇怪,他没给我打电话。
3. Fortunately, I found the book that I?d lost.
幸亏我找到了已丢失的那本书。
二、常见的作插入语的形容词或其短语
true真的, funny真可笑, strange to say说也奇怪, needless to say不用说, most impor tant of all最为重要, worse still更糟糕的等。
1. Strange to say (或True), he should he done such a thing.
说也奇怪(或真的),他竟然做出这样的事。
2. Most important of all, you each over?fulfilled your own task.
更为重要的,你们各自超额完成了自己的任务。
三、常用作插入语的介词短语
in a few words(或in sum, in short)简而言之, in other words换句话说, in a sense在某种意义上, in general一般说来, in my view在我看来, in his opinion(judgment)按照他的意见(判断), in conclusion总之, in summary概括地说, in fact事实上, in the first place首先, in addition此外, of course当然, to our knowledge据我们所知, to my joy(delight, satisfaction)使我欣慰(高兴、满意)的, to their surprise(astonis hment, amazement)使他们惊奇的, to her regret (disointment)使她遗憾(失望)的, for instance(或example)例如, as a matter of fact事实上等。
跪求高考英语考到的几大重要动词时态
高考英语应该掌握的不及物动词
英语中按动词后可否直接跟宾语,可把动词分成及物动词和不及物动词。
不及物动词:字典里词后标有vi. 的就是不及物动词。不及物动词后不能直接跟有动作的对象(即宾语)。若要跟宾语,必须先在其后添加上某个介词,如to,of ,at后方可跟上宾语。具体每个动词后究竟加什么介词就得联系动词短语了.
常用的不及物动词 ear ,Appear calm come ,Come easy (safe)
go ,Go mad (crazy, bad, sour, wrong, crazy, hungry, blind) get ,Get angry (ill, wet, excited, married, paid) fall ,Fall asleep( fall ill, fall short, fall flat) feel ,Feel good (sleepy) keep ,Keep quiet (silent) look ,Look fit (well, young, tired)
make, Make certain (sure, ready, a good teacher) prove ,Prove an effective method (correct, accurate) remain ,Remain still (unchanged) rest,Rest satisfied (content) rise, Rise red seem ,Seem hy stand ,Stand still
stay ,Stay young (stay fresh, the same) turn, Turn teacher =become a teacher (yellow) turn out ,Turn out true 用法举例
Look carefully! (注意:carefully 是副词,不是名词,故不作宾语) look at 看…….+宾语 Look at me carefully! (me是代词,作宾语) (at是小范围 in是大范围)
如: The students work very hard.学生们很努力地学习。 She apologized to me again. 她再次向我道歉。
The accident hened yesterday evening.昨天晚上发生了事故。 与及物动词的区别
及物动词与不及物动词的区别从是否需要宾语来分,实义动词分为及物动词和不及物动词两类。
1)及物动词 后面必须跟宾语意义才完整的实义动词,叫做及物动词(transitive verb)。如: I believe that the committee will consider our suggestion.我相信委员会将会考虑我们的建议。
“How long can I keep the book ?”Harry asked.哈里问:“这本书我可以借多久?” 2)不及物动词 本身意义完整后面不须跟宾语的实义动词,叫做不及物动词(intransitive verb)。如: Birds fly.鸟会飞。
It hened in June 1932.这件事发生于一九三二年六月。 My watch stopped.我的表停了。
She spoke at the meeting yesterday evening. 她在昨天晚上的会上发了言。 3)兼作及物动词和不及物动词 英语里有不少实义动词可以兼作及物动词和不及物动词。这样的动词又有两种不同的情况:
a)兼作及物动词和不及物动词时,意义不变。试比较: Shall I begin at once?我可以立刻开始吗?(begin作不及物动词)
She began working as a librarian after she left school.她毕业后当图书馆管理员。(begin作及物动词)
When did they lee Chicago?他们是什么时候离开芝加哥的?(lee 作及物动词) They left last week. 他们是上周离开的。(left 作不及物动词) b)兼作及物动词和不及物动词时,有时意义不尽相同。如: Wash your hands before meals.饭前要洗手。 Does this cloth wash well? 这布经得起洗吗?
4) 与汉语的比较 有时英语动词的及物和不及物的用法,与汉语的用法不一样,请注意下列两种情况:
a)有的动词在英语里只能用作不及物动词,而汉语则可用作及物动词,如arrive到达,agree同意,1isten听。英语里这些动词后面常接介词。如:
We arrived at the railway station at noon.我们于中午到达火车站。(at不能省去)(比较:We reached the railway station at noon.)
Everybody listened to the lecture with great interest.每个人都很有兴趣地听讲课。(to不可省去)(比较:We all heard the lecture.)
Do they agree to the plan?他们同意这个吗?(to不可省去)
b)有的动词在英语里能用作及物动词,而在汉语里则不能用作及物动词,如serve为…服务。 Our children are taught to serve the people wholeheartedly.我们的儿童被教以全心全意为人民服务
及物动词后可以加宾语,不及物动词后不可以加宾语
动词的及物不及物是在英语学习中必须解决的首要问题。动词及物与不及物通常有以下几种情况:
a.主要用作及物动词。及物动词后面必须跟宾语。可以用于:"主+谓+宾";"主+谓+双宾";"主+谓+宾+宾补"结构。如:
He reached Paris the day before yesterday. Please hand me the book over there. They asked me to go fishing with them.
类似的还有:buy, catch, invent, found, like, observe, offer, prevent, promise, raise, find, forget, receive, regard, see, say, seat, supply, select, suppose, show, make, take, tell.... b.主要用作不及物的动词。不及物动词后面不跟宾语。只能用于:"主+谓"结构。 This is the room where I once lived.
类似的还有:agree, go, work, listen, look, come, die, belong, fall, exist, rise, arrive, sit, sail, hurry, fail, succeed....
c.既可以用作及物又可以用作不及物的动词,其意义不变。如begin 都是作"开始"讲。everybody , our game begins. let us begin our game.
类似的还有:start, answer, sing, close, consider, insist, read, learn, prepare, pay, hurt, improve....
d.既可以用作及物又可以用作不及物的动词,其意义完全不同。
这类动词作不及物动词是一个意义;而作及物动词时却是另一个意义。如lift作不及物动词时是指烟雾的"消散"。we saw the mountain when the clouds lifted. 作及物动词时是"升高;举起"。 He lifted his glass and drank.
类似的还有:beat vi.跳动 vt. 敲、打; grow vi.生长 vt. 种植 play vi.玩耍 vt. 打(牌、球),演奏 smell vi.发出(气味) vt. 嗅 ring vi.(电话、铃)响vt.打电话 speak vi.讲话 vt. 说(语言) hang vi. 悬挂 vt. 绞死 operate vi.动手术 vt. 操作 需要注意的一点是:少数不及物动词唯一可跟的宾语是同源宾语,如:I dreamed a dream last night.
一些动词应用中只能用主动表示被动。
1、 Need, want, require(要求,需要), deserve(应得,值得), be worth值得),not bear(经不住) 后面接doing主动表被动。
The book is worth reading. 这本书值得一读。
The old building requires repairing. 这座古建筑需要修了。
These young seedlings will require/need looking after (=need to be looked after) carefully.?这些幼苗将需要小心的照管。 Your hair wants/needs cutting (needs to be cut).?你的头发该剪了。
2、不定式作定语,放在被修饰词后面,与前面被修饰的名词或代词有动宾关系,又在句子中与另一名词或代词有主谓关系,不定式要用主动表被动含义。
I he much work to do. 我有许多要做的事情。(与work有动宾关系,与I有主谓关系) Tom is looking for a room to live in. Tom在找一间住的房间。(与room有动宾关系,与Tom 有主谓关系)
He has a family to support.?他要维持一个家庭。(与family有动宾关系,与he有主谓关系) 3、不定式修饰作表语和宾语补足语的形容词时,结构:主语+系动词+形容词 + 不定式; 动词+宾语+形容词+不定式。如果形容词是表示难易、利弊等含义,如
difficult, easy, comfortable(舒适的), convenient(便利的,方便的), hard, cheap, expensive, 等,不定式用主动表被动。
The question is difficult to answer. 这个问题很难回答。 The work is easy to do. 这项工作很好做。
I found the car comfortable to ride in. 我觉得这种车很好坐。 That makes poetry difficult to write. 那就使得诗很难写。
4、在be to结构中的一些不定式:这种结构中的不定式通常应用主动表被动。下列动词用不定式的主动形式表示被动意义: Who is to blame for starting the fire?这场火灾应由谁负责?
You are to blame for the accident. 你应为这事受动责备。 The house is to let.此房出租。
A lot remains to do.还剩下许多事情要做。
5、系动词没有被动形式,但有些系动词常表示被动意义。常见的有taste(吃起来), sound (听起来), prove(证明是), feel(摸上去感到), look(看起来),smell(闻起来)等。
6.一些与can''t(不能)或won''t(不会)连用的动词。常用的有: lock(锁住), shut(关上) , open(打开), act(上演), write(写),cut(砍,切),wear(穿,戴)等,用作不及物动词时,用主动表被动。
7、一些动词如sell(销售) , wash(洗), clean(打扫), burn(燃烧), cook(煮)等与副词如well(好), easily(容易地), perfectly(十分地)等连用 ,描会事物的特性,用主动表被动,结构是主语+动词+加副词。例如:The book sells well.这种书很畅销 These clothes wash easily.?这些衣服很易洗。The pen writes well. 这笔很好写。
8、主语much, a great deal, little, what等,其表语如是不定式,则用不定式的主动表被动。 What is to do? 做什么? Much is to do. 太多要做的事。
9、在“there be”句型中作主语的定语如果现在分词时,所用的现在分词要用主动表被动意义。 There is nothing doing these days. 这些天没事干。 I see there’s a good idea planning. 我知道又在打好主意。
三、完成时态
完成时态通常表示已完成或从事的动作。它可分为:
1. 现在完成时
(1)现在完成时用来表示对目前状况仍有影响的,刚刚完成的动作(常与yet,already,just连用),或者过去某一时刻发生的,持续到现在的情况(常与for,since连用)。例如:
1)I he just finished my homework.
2)Mary has been ill for three days.
(2)常与现在完成时连用的时间状语有:since, for, during, over等引导出的短语;副词already, yet, just, ever, now, before, often, lately, recently等;状语词组this week (morning, month, year), so far, up to now, many times, up to the present等。例如:
1)I hen’t been there for five years.
2)So far, she hasn’t enjoyed the summer vacation.
3)There he been a lot of changes since 18.
(3)完成时态可用在下列结构中:
This (That, It) is (was) the first (second…) time +定语从句;This (That, It) is (was) the only (last) + n +定语从句;This (That, It) is (was) +形容词最高级+ n +定语从句。如果主句的谓语动词是一般现在时,从句的谓语动词通常用现在完成时;如果主句谓语动词是一般过去时,从句谓语动词通常用过去完成时。例如:
(1)This is one of the rarest questions that he ever been raised at such a meeting.
(2)There was a knock at the door. It was the second time someone had interrupted me that evening.
2. 过去完成时
(1)表示过去某时间前已经发生的动作或情况,这个过去的时间可以用by,before等介词短语或一个时间状语从句来表示;或者表示一个动作在另一个过去动作之前已经完成。例如:
1)We had just had our breakfast when Tom came in.
2)By the end of last year they had turned out 5, 000 bicycles.
(2)动词expect, hope, mean, intend, plan, suppose, wish, want, desire等用过去完成时,表示过去的希望、预期、意图或愿望等没有实现。例如:
I had meant to take a good holiday this year, but I wasn’t able to get away.
另外两种表示“过去想做而未做的事”的表达方式是:
1)was / were + to he done sth, 例如:
We were to he come yesterday, but we couldn’t.
2)intended (expected, hope, meant, planned, supposed, wished, wanted, desired) + to he done sth, 例如:
I meant to he told you about it, but I forgot to do so.
(3)过去完成时常用于以下固定句型:
1)hardly, scarcely, barely + 过去完成时+ when + 过去时。例如:
Hardly had I got on the bus when it started to move.
2)no sooner +过去完成时+ than +过去时。例如:
No sooner had I gone out than he came to see me.
3)by (the end of ) +过去时间,主句中谓语动词用过去完成时。例如:
The experiment had been finished by 4 o’clock yesterday afternoon.
3. 将来完成时
将来完成时表示在将来某一时刻将完成或在另一个未来的动作发生之前已经完成的动作;也可以用来表示一种猜测。常与将来完成时连用的时间状语有:by (the time / the end of ) + 表示将来时间的短语和句子;before (the end of ) + 表示将来时间的词语或句子;when, after等加上表示将来动作的句子等。例如:
1)By this time tomorrow you will he arrived in Shanghai.
2)I shall he finished this composition before 9 o’clock.
3)When we get on the railway station, the train will probably he left.
4. 完成进行时
完成进行时是完成时的强调形式,有现在完成进行时,过去完成进行时,将来完成进行时。
(1)现在完成进行时表示过去某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态一直延续到过去某一时刻。例如:
I he been looking for my lost book for three days, but I still hen’t found it.
(2)过去完成进行时表示过去某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态一直延续到过去某一时刻。例如:
It had been raining cats and dogs for over a week and the downpour had caused landslides in many places.
(3)将来完成进行时表示在将来某一时刻之前开始的一个动作或状态一直延续到将来某一时刻。例如:
By the time you arrive tonight, she will he been typing for hours.









